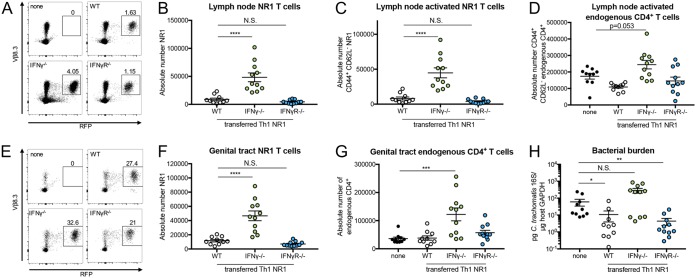
FIG 4.
IFN-γ production by NR1 T cells is necessary for NR1-mediated protection against C. trachomatis. IFN-γ−/− mice received 106 Th1-skewed WT, IFN-γ−/−, or IFN-γR−/− RFP NR1 T cells 1 day prior to infection with 5 × 106 IFU C. trachomatis. (A to D) Five days postinfection, uterine draining lymph nodes were assessed by flow cytometry for (A and B) NR1 T cells, (C) activated NR1 T cells, and (D) activated endogenous CD4+ T cells (CD44+ CD62L− of CD4+ RFP−). (E to H) Upper genital tracts were assessed by flow cytometry for (E and F) NR1 T cells and (G) endogenous CD4+ T cells and by qPCR for (H) bacterial burden. Data were pooled from results of two independent experiments performed with at least five mice per group and were analyzed by ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test (B to D, F, and G) or by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple-comparison test (H). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; N.S., not significant.