FIG 3.
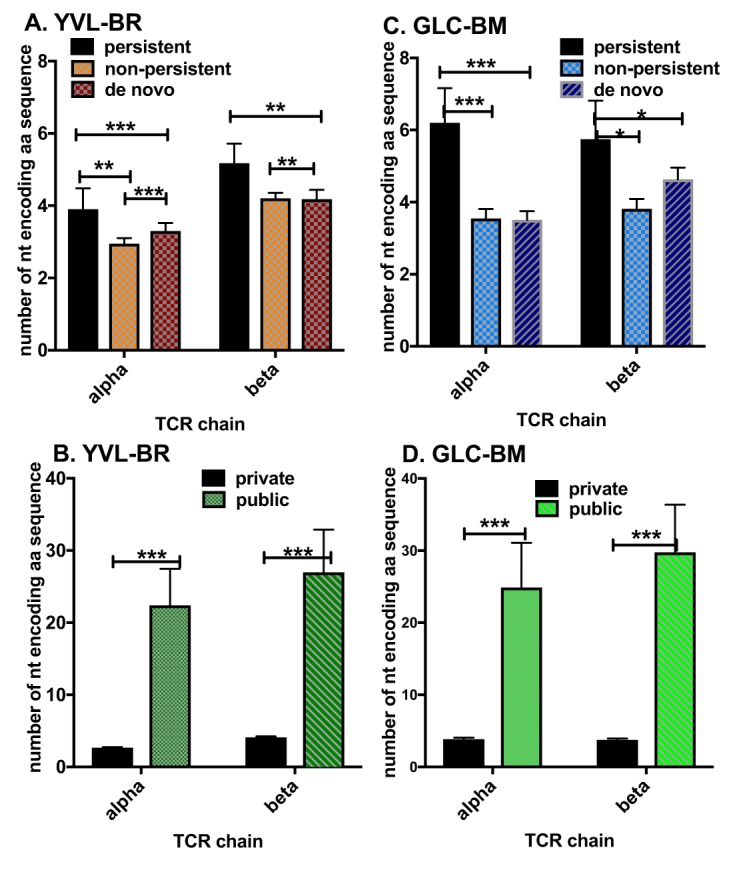
Convergent recombination drives selection of persistent but not nonpersistent TCR repertoire: increased usage in CDR3 of amino acids derived by multiple different nucleotide sequences. Shown is the number of nucleotides encoding amino acid sequence in CDR3 of YVL-BR-specific (A and B) and GLC-BM-specific (C and D) TCRα and TCRβ of persistent, nonpersistent, and de novo repertoires (A and C) and private versus public clonotypes (B and D). (A public TCR is defined as more than one donor using that clonotype based on amino acid sequence.) Data were analyzed by multivariant two-way ANOVA with correction for multiple comparisons. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001. Error bars are SEM.
