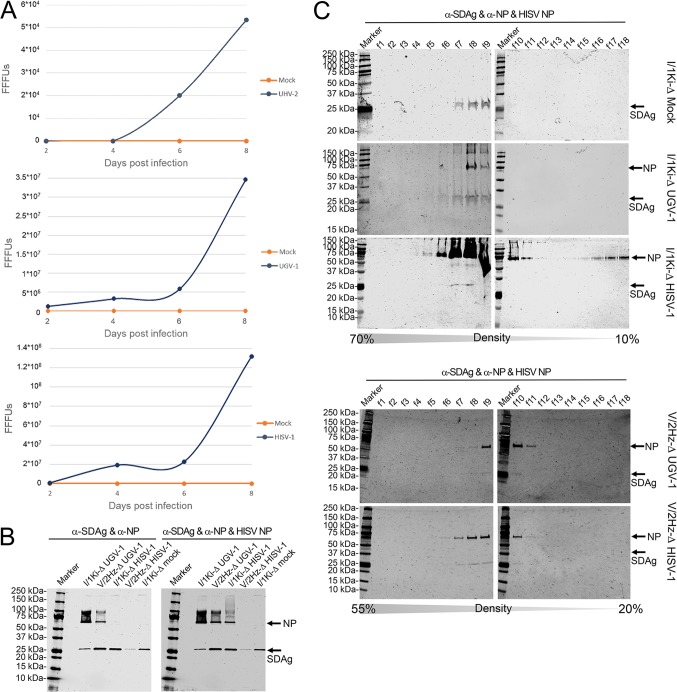
FIG 6.
Superinfection of permanently SDeV-infected boid cells (I/1Ki-Δ and V/2Hz-Δ) induced production of infectious SDeV particles. (A) Supernatant collected from mock-, UHV-2 (top), UGV-1 (middle), and HISV-1 (bottom) superinfected I/1Ki-Δ cells at 2, 4, 6, and 8 days postinfection (dpi) were titrated on clean I/1Ki cells. The y axis shows the number of fluorescent focus-forming units (FFFUs) per milliliter of culture medium. (B) Supernatants collected from mock-, UHV-2, UGV-1, and HISV-1 superinfected I/1Ki-Δ cells and UGV-1 and HISV-1 superinfected V/2Hz-Δ cells were pelleted by ultracentrifugation and analyzed by Western blotting. The left panel shows anti-SDAg staining, and the right panel shows anti-SDAg, anti-reptarenavirus NP, and anti-hartmanivirus NP staining. (C) Pelleted supernatants collected from mock-, UGV-1, and HISV-1 superinfected I/1Ki-Δ cells and UGV-1 and HISV-1 superinfected V/2Hz-Δ cells were subjected to density gradient ultracentrifugation, and the fractions collected from the bottom of the tubes were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-SDAg and anti-reptarenavirus NP staining (for mock and UGV-1) or anti-SDAg and anti-hartmanivirus NP staining (for HISV-1). The arrows indicate the locations of SDAg and reptarenavirus or hartmanivirus NP. Precision Plus Protein Dual Color Standards (Bio-Rad) served as the markers for both panels B and C, and the results were recorded using the Odyssey infrared imaging system (Li-Cor).