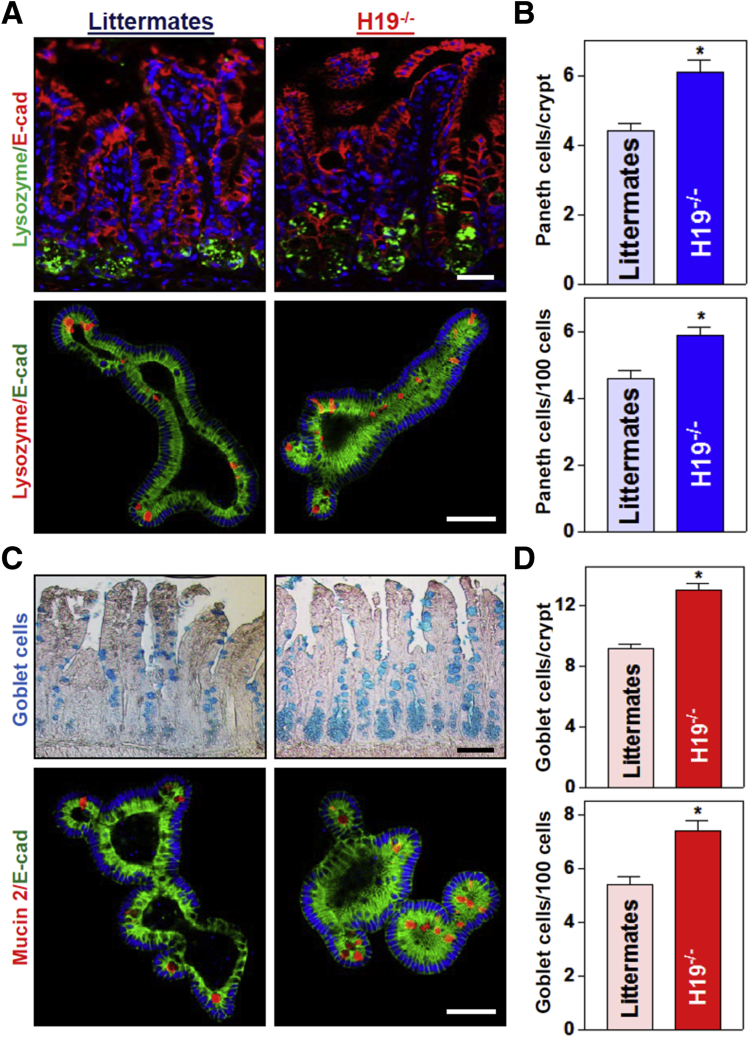
Figure 2.
Targeted deletion of H19 in mice increases the numbers of Paneth and goblet cells in the intestinal epithelium. (A) Immunostaining of Paneth cells (lysozyme-positive cells). Top: Paneth cells in the small intestinal mucosa of H19-/- and control littermate mice (green); bottom: Paneth cells in small intestinal organoids isolated from H19-/- and littermate mice (red). Scale bars: 50 μm. (B) Quantitative data of lysozyme-positive cells in the small intestinal epithelium described in panel A. Values are the means ± SEM (n = 5). *P < .05 compared with control littermate mice. (C) Immunostaining of Goblet cells (Alcian blue staining in vivo; mucin 2–positive cells ex vivo). Top: Goblet cells in the small intestinal mucosa of H19-/- and control littermate mice (blue); bottom: Goblet cells in small intestinal organoids isolated from H19-/- and littermate mice (red). Scale bars: 50 μm. (D) Quantitative data of mucin 2–positive cells in the small intestinal epithelium described in panel C. Values are the means ± SEM (n = 5). *P < .05 compared with control littermate mice. E-cad, E-cadherin.