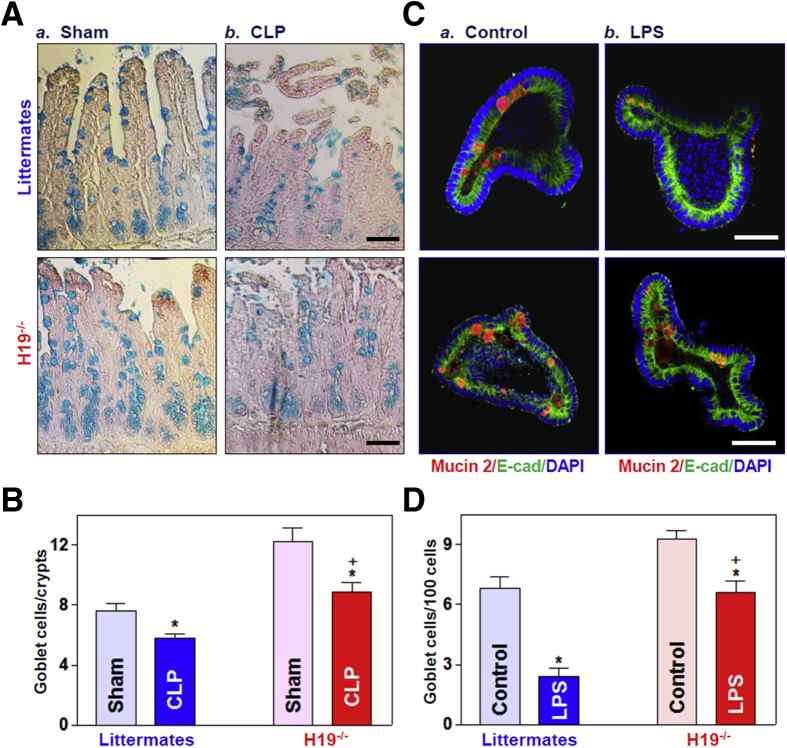
Figure 5.
H19 deletion protects Goblet cells against CLP- and LPS-induced stress in vivo and ex vivo. (A) Goblet cells were examined by Alcian blue staining in the small intestinal mucosa of H19-/- and control littermate mice (a) Sham; and b) CLP) exposed to CLP for 24 hours. Scale bars: 50 μm. (B) Quantitative data of goblet cells in the small intestinal mucosa of mice treated as described in panel A. Values are the means ± SEM (n = 5). *,+P < .05 compared with sham-treated mice and littermate mice exposed to CLP, respectively. (C) Immunostaining of goblet cells (mucin 2–positive cells) in intestinal organoids exposed to LPS (20 ng/mL) for 5 days (red). Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) Quantitative results of goblet cells in intestinal organoids treated as described in panel C: a) Control; and b) LPS. Values are the means ± SEM (n = 5). *,+P < .05 compared with controls (without LPS treatment) and organoids (from littermate mice) exposed to LPS, respectively. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; E-cad, E-cadherin.