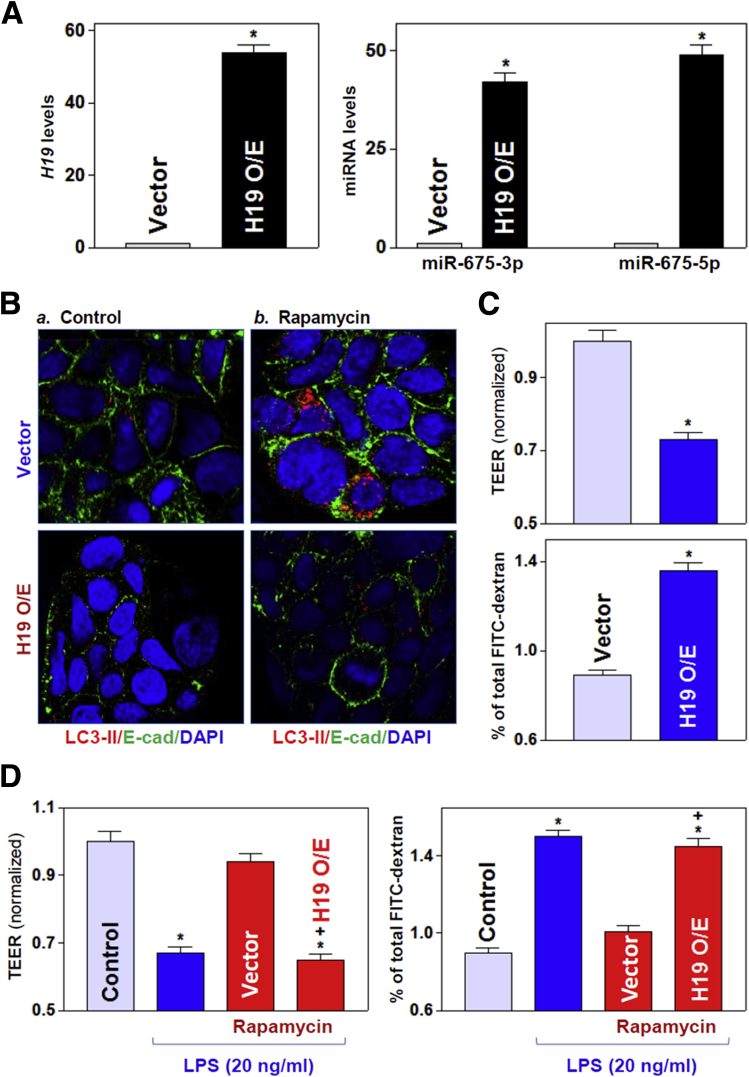
Figure 7.
Ectopically expressed H19 prevents induced autophagy and disrupts the epithelial barrier function in vitro. (A) Levels of H19 (left) and miR-675 (right) in cultured IECs transfected with the H19 expression vector and measured 48 hours later. Values are relative to those for the control (vector) and are the means ± SEM from triplicate experiments. *P < .05 compared with the vector. (B) Immunostaining of LC3-II in cells exposed to rapamycin (50 ng/mL) for 24 hours (red). Twenty-four hours after transfection with a control vector or a vector to overexpress H19, cells were exposed to rapamycin: a) Coontrol; and b) Rapamycin. Three experiments were performed that showed similar results. (C) Changes in epithelial barrier function were assessed by monitoring changes in TEER (top) and FITC-dextran paracellular permeability (bottom) in cells treated as described for panel A. TEER assays were performed on 12-mm Transwell filters; paracellular permeability was assayed by using the membrane-impermeable trace molecule FITC dextran, which was added to the insert medium. Values are the means ± SEM from triplicate experiments. *P < .05 compared with the vector. (D) Changes in barrier function in cells treated for 24 hours with LPS (20 ng/mL) alone or with LPS plus rapamycin in control cells as in cells overexpressing H19. *,+P < .05 compared with control and cells treated with LPS plus rapamycin, respectively. O/E, overexpression. DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; E-cad, E-cadherin.