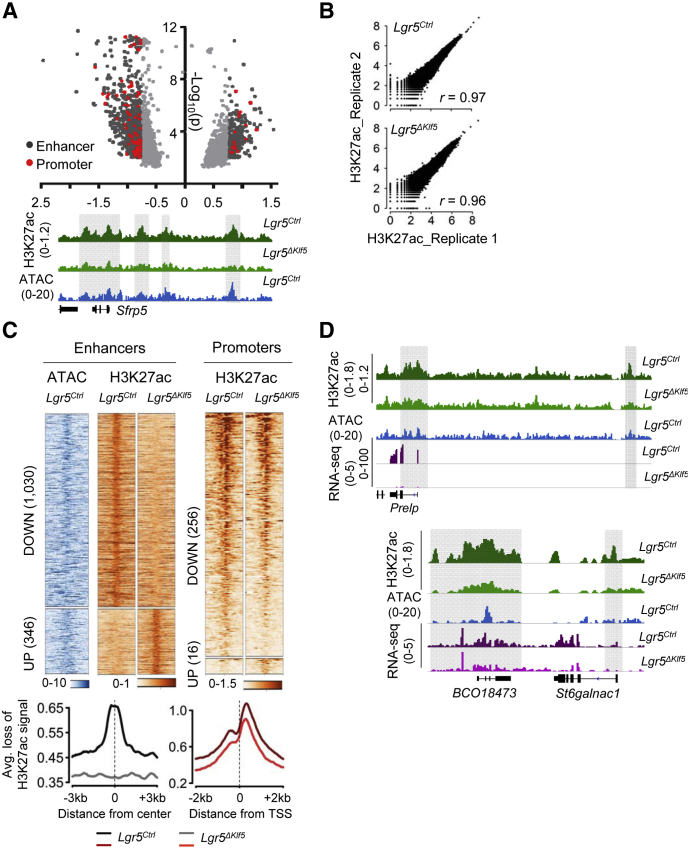
Figure 7.
Loss of Klf5 in intestinal stem cells leads to depletion of H3K27ac at genomic loci. (A) Genome-wide differential H3K27ac analysis27 reveals up- and downregulated regions in Lgr5ΔKlf5. Volcano plot shows all regions achieving P < .01 with fold-change (FC) depicted by shades of gray (light gray FC <1.7, dark gray FC ≥1.7); red dots mark promoters. Representative IGV tracks for H3K27ac28 and ATAC-seq (blue) at Sfrp5 in Lgr5Ctrl and Lgr5ΔKlf5 or Lgr5Ctrl ISCs, respectively. The shaded boxes mark regions of H3K27ac loss at promoter and putative enhancers. (B) Scatter plots show correlation between duplicate Lgr5Ctrl or Lgr5ΔKlf5 H3K27ac ChIP-seq samples. r is the Pearson correlation coefficient. (C) Heatmaps represent ATAC-seq (in Lgr5Ctrl ISCs; GSE83394) and H3K27ac at 1030 down and 346 upregulated enhancers in Lgr5ΔKlf5 compared with control ISCs (FC ≥1.7, P < .01). H3K27ac at 256 and 16 down and upregulated promoters, respectively, in Lgr5ΔKlf5 is depicted to the right. Aggregate plots show average signal intensities at enhancers (left) and promoters depleted for H3K27ac in Lgr5ΔKlf5. (D) Representative IGV tracks for H3K27ac ChIP-seq,28 ATAC-seq (blue), and RNA-seq (purple) at Prelp and St6galnac1 loci. The shaded regions depict loss of H3K27ac at promoters or enhancers.