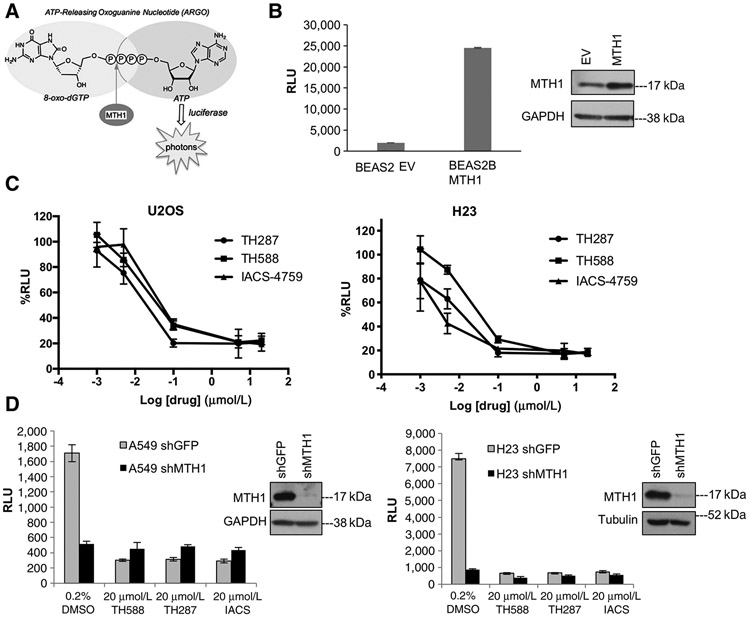
Figure 1.
The ARGO probe–based assay is an accurate measure of MTH1-specific 8-oxodGTPase activity. A, Schematic showing how cleavage of the chimeric ARGO probe (with 8-oxodG and A base moieties) by MTH1 8-oxodGTPase activity generates ATP that can then be detected via a luciferase-based luminescent signal. B, ARGO probe–generated luminescence (in relative luminescence units, RLU) from lysates made from stable MTH1-ovexpressing BEAS2B cells or their empty vector (EV)-transduced counterparts. Each sample was run in triplicate and data are representative of a minimum of n = 2.Arepresentative Western blot run on 10 μg total protein lysates from these cell lines, with the MTH1 signal and GAPDH loading control, is shown to the right of the graph. Error bars, ± SD. C, The percent decreases in ARGO probe-generated luminescence in U2OS and H23 lysates by the three indicated MTH1 inhibitors. The log-transformed drug concentration range is indicated on the x-axis. Each concentration was run in triplicate, and the signal at each concentration is normalized to signal from the counterpart vehicle-treated lysates. Error bars, ± SD. D, Comparison of effects on ARGO probe–generated luminescence produced by shRNA-mediated MTH1 depletion versus the first-in-class MTH1 inhibitors. Data are representative of a minimum of n = 2, with each sample run in triplicate. Western blotting on 10 μg of total protein from A549 lysates and 20 mg total protein from H23 lysates, with the MTH1 signal and GAPDH or tubulin as loading controls, is shown to the right of the graph, to establish levels of MTH1 protein knockdown.