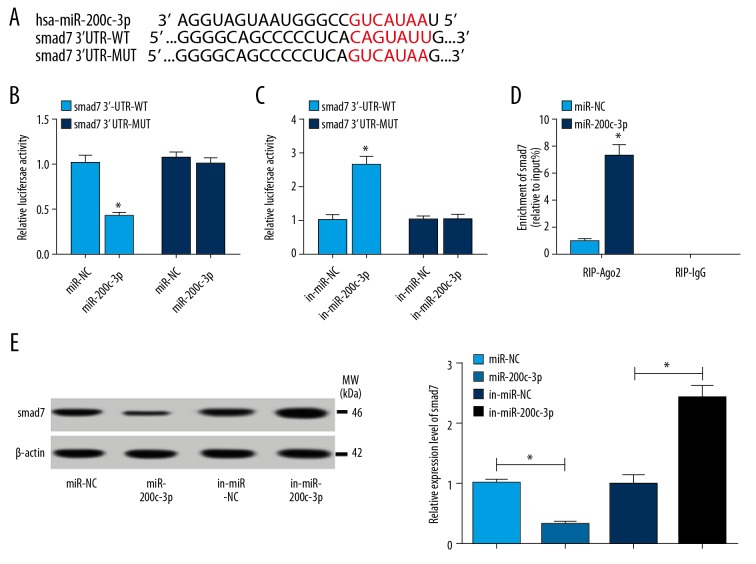
Figure 4.
(A–E) smad7 was a target of miR-200c-3p. (A) The binding sites between miR-200c-3p and smad7 were analyzed by online software TargetScan. (B, C) Luciferase reporter assay was executed to verify the interaction of miR-200c-3p and smad7 in hBMSCs. (B) hBMSCs were transfected with smad7 3′UTR-WT sequences containing binding sites of miR-200c-3p or smad7 3′UTR-MUT sequences and miR-200c-3p mimics, miR-NC as a control. (C) hBMSCs were transfected with smad7 3′UTR-WT sequences containing binding sites of miR-200c-3p or smad7 3′UTR-MUT sequences and miR-200c-3p inhibitor, in-miR-NC as a control. (D) RIP assay was conducted to further confirmed the relationship between miR-200c-3p and smad7. (D) The protein level of smad7 was determined by western blot assay after miR-200c-3p overexpression or inhibition. Data were presented as mean±standard deviation (SD) based on 3 independent replicates. * P<0.05. hBMSCs – human bone mesenchymal stem cells; RIP – RNA immunoprecipitation.