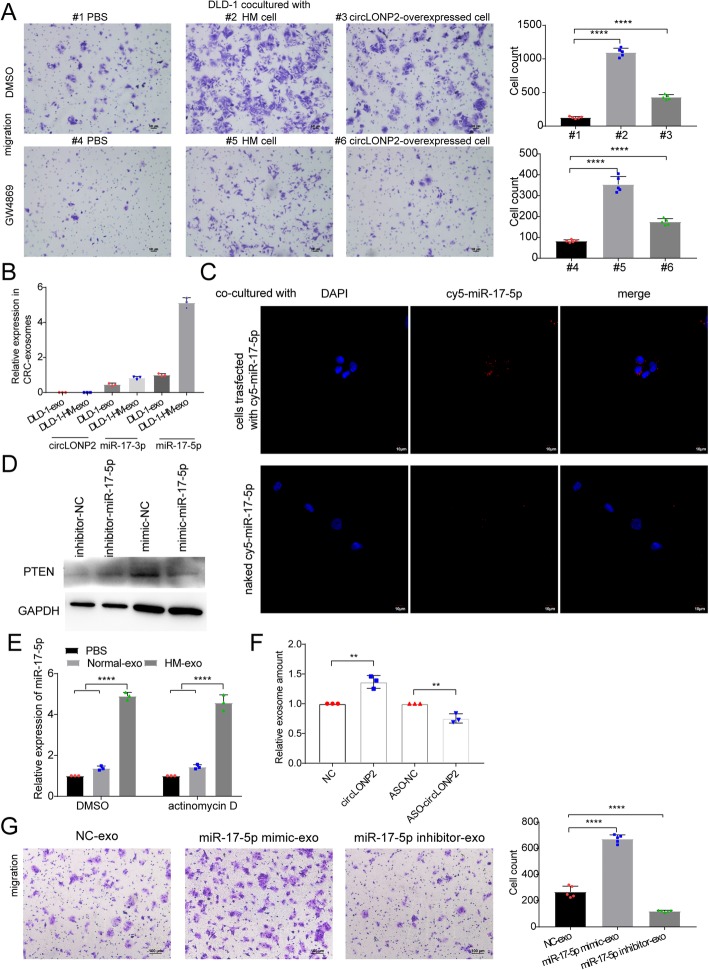
Fig. 7.
circLONP2-driven intercellular transfer of miR-17-5p by exosomes disseminates high metastatic potential. a DLD-1 cells co-cultured with HM or circLONP2-overexpressed cells showed enhanced migration ability, and this effect could be attenuated by GW4869 treatment. b Detecting the expression level of circLONP2, miR-17-3p and miR-17-5p in CRC-derived exosomes by RT-qPCR, normalized to λ-polyA or cel-miR-39. c Red fluorescence could be observed in almost every recipient cell co-cultured with cells transfected with cy5-miR-17-5p, whereas few fluorescence could be observed in recipient cells co-incubated with naked cy5-miR-17-5p, revealed by IF. d The expression of PTEN, one of classical downstream target of miR-17-5p, was significantly changed in recipient cells co-incubated with exosomes electroporated with miR-17-5p inhibitors or mimics. e Increase of miR-17-5p level in recipient cells after incubation with HM-exosomes could not be affected by actinomycin D treatment, normalized to U6. f The exosome amounts could be significantly changed upon overexpression or depletion of circLONP2, revealed by microBCA analysis. g CRC cells provided with exosomes containing miR-17-5p mimics exhibited enhanced metastatic ability, while exosomes containing miR-17-5p inhibitors showed opposite effect. All experiments were repeated for three times, data were shown as mean ± SD, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001 in one-way ANOVA (a, e-g), or Mann-Whitney U test (f)