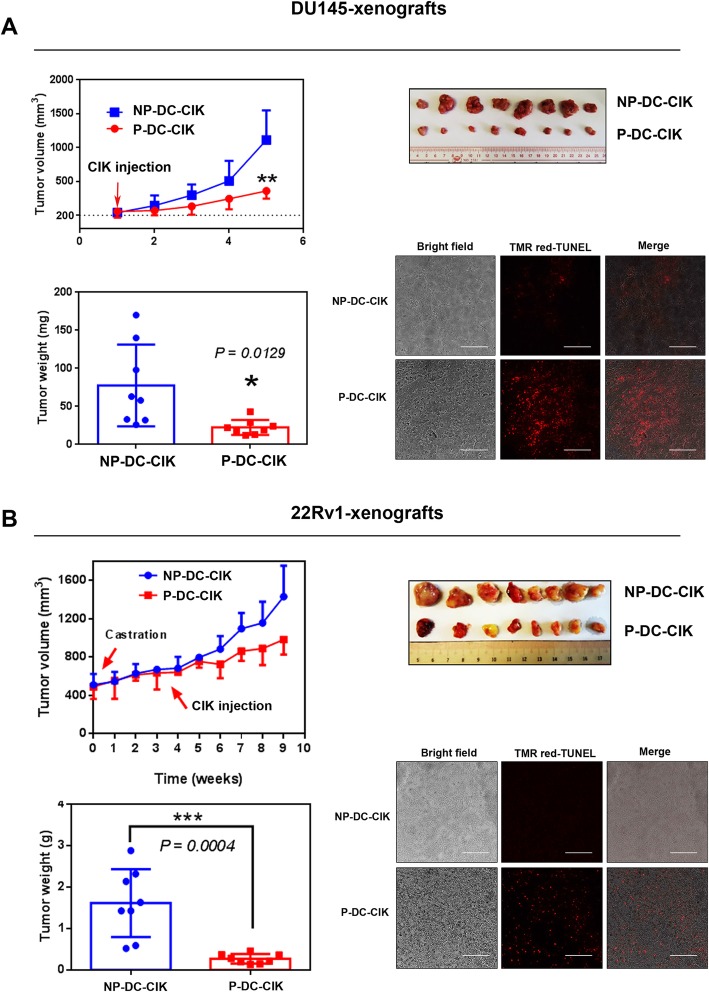
Fig. 7.
Anti-tumor activity of intratumoral injection of peptide-loaded DC-activated CIK cell preparations (P-DC-CIK) or non-peptide-loaded NP-DC-CIK cell preparations on two prostate cancer xenograft models derived from prostatospheroids. a DU145 xenografts. Upon intratumoral injection of P-DC-CIK, DU145 xenograft tumors grew very slowly. b 22Rv1 xenografts. Castration-refractory 22Rv1-CRPC xenografts were induced in SCID mice bearing 22Rv1 xenografts by castration when the tumor sizes reached about 5 mm3. Similar to DU145 xenografts, intratumoral injection of P-DC-CIK could significantly suppress the tumor growth as compared to injection of NP-DC-CIK control. Histochemical TUNEL staining revealed that significant increases of TMR red-labeled apoptotic cells were detected in both DU145 and 22Rv1 xenografts treated with P-DC-CIK as compared to NP-DC-CIK. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001 versus NP-DC-CIK control