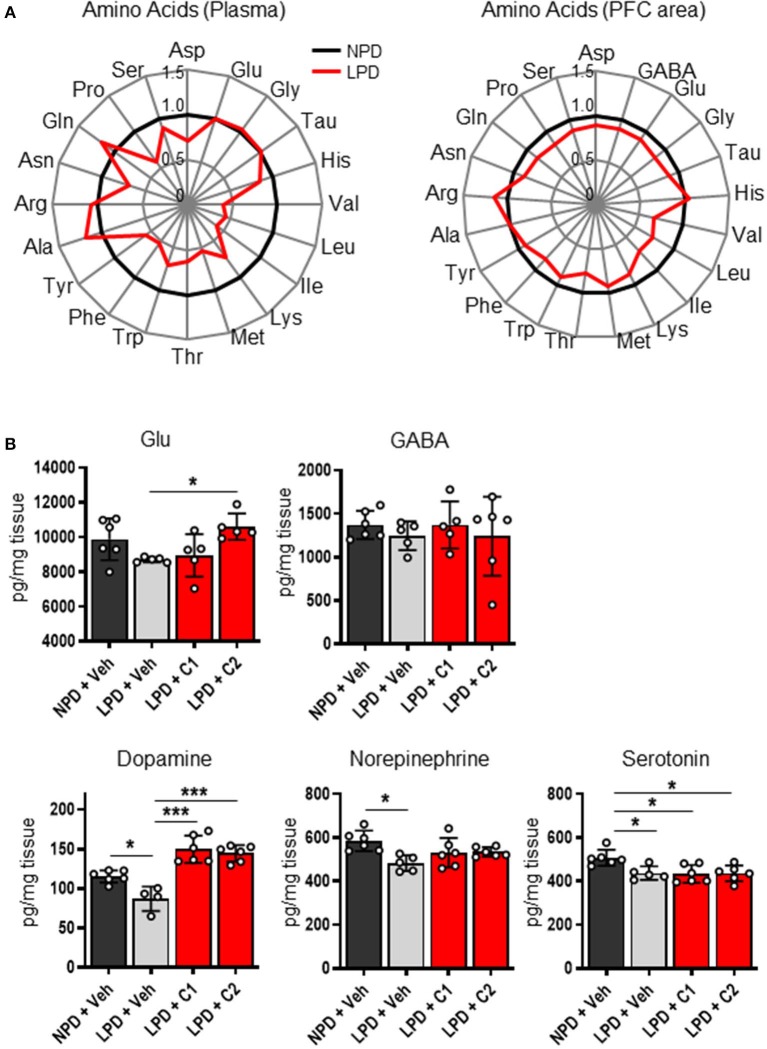
Figure 2.
The concentrations of amino acids and neurotransmitters in the plasma and brain were decreased by LPD. (A) Radar charts of amino acids in aged B6 mice. The average of each amino acid concentration as normalized values in the plasma (left) and prefrontal cortex area (PFC area; right) are expressed. (B) Mean neurotransmitter concentrations in the PFC area after sacrifice in each group. The Glu concentration [F(3, 17) = 4.2, p < 0.05] was significantly lower in the LPD + C2 group than in the LPD + Veh group (*p < 0.05). The dopamine concentration [F(3, 18) = 23.9, p < 0.001] was significantly lower in the LPD + Veh group than in the NPD + Veh group (*p < 0.05), in the LPD + Veh group than in the LPD + C1 group (***p < 0.001), and in the LPD + Veh group than in the LPD + C2 group (***p < 0.001). The norepinephrine concentration [F(3, 19) = 4.5, p < 0.05] was significantly lower in the LPD + Veh group than in the NPD + Veh group (*p < 0.05). The serotonin concentration [F(3, 19) = 5.7, p < 0.01] was significantly lower in the LPD + Veh group than in the NPD + Veh group (*p < 0.05), in the LPD + C1 group than in the NPD + Veh group (*p < 0.05), and in the LPD + C2 group than in the NPD + Veh group (*p < 0.05). Error bars and dots indicate SD and scores of individual mice, respectively.