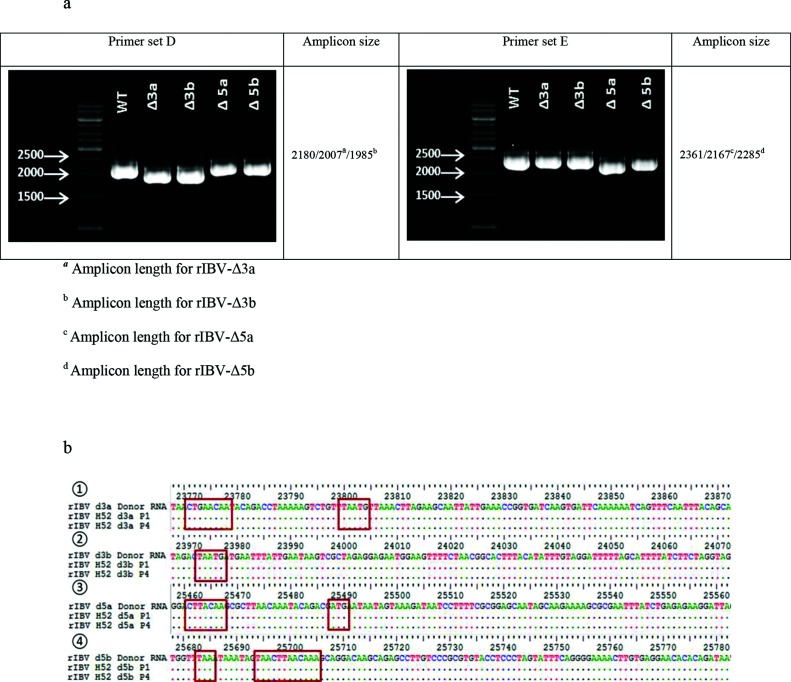
Fig. 3.
Genetic characterization and stability of rescued recombinant virus rIBV-Δ3a, rIBV-Δ3b, rIBV-Δ5a and rIBV-Δ5b. (a) Electrophoresis showing the amplicons obtained after the amplification of cDNA templates of viral RNA extracted from the AF of ECEs inoculated with P1 of virus rIBV-Δ3a, rIBV-Δ3b, rIBV-Δ5a and rIBV-Δ5b using primer sets that span the genomic area of accessory genes 3 (primer set D) and 5 (primer set E). Expected amplicon sizes are indicated in the right columns. (b) Sequences and locations of the genomic regions in which the mutations were introduced in order to selectively delete the accessory genes. (1) Comparison of the sequences obtained from P1 and P4 of rIBV-Δ3a. The genomic region shown is the junction between the spike gene and the 3b gene; the TRS (CTGAACAA) now used for the transcription of genes 3b and E and the overlap between the S gene stop codon and the 3b gene codon start (TAATG), respectively, are highlighted in the red squares. (2) Comparison of the sequences obtained from P1 and P4 of rIBV-Δ3b. The genomic region shown is the junction between the 3a and the E genes; the overlap between the 3a gene stop codon and the E gene start codon (TAATG) is highlighted in the red square. (3) Comparison of the sequences obtained from P1 and P4 of rIBV-Δ5a. The genomic region shown is the junction between the intergenic region and the 5b gene; the TRS (CTTAACAA) and the start codon (ATG) now used for the transcription of gene 5b, respectively, are highlighted in the red squares. (4) Comparison of the sequences obtained from P1 and P4 of rIBV-Δ5b. The genomic region shown is the junction between the 5a and the 5b genes; the two stops codon (TAA) introduced to prevent the transcription of gene 5b and the TRS (CTTAACAA) used for the transcription of gene N, respectively, are highlighted in the red squares.