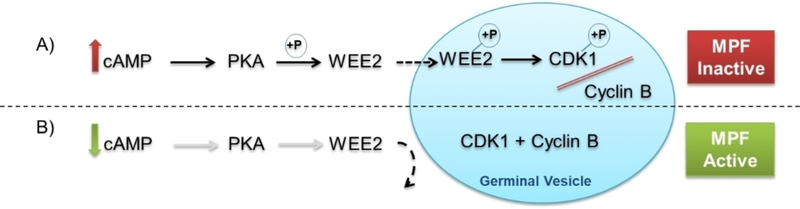
Figure 1.
A) Maintenance of meiosis arrest in the prophase I oocyte is facilitated by elevated cAMP. Active PKA phosphorylates WEE2 which in turn translocates into the germinal vesicle (GV) to phosphorylate CDK1, a form that prevents complexing with cyclin B and formation of active MPF. B) A decline in cAMP inactivates PKA and the phosphorylating activity on WEE2 so that it is unable to enter the GV. Without an inhibitory phosphate in place, CDK1 complexes with cyclin B to form MPF and drive meiosis resumption.