Fig. 10.
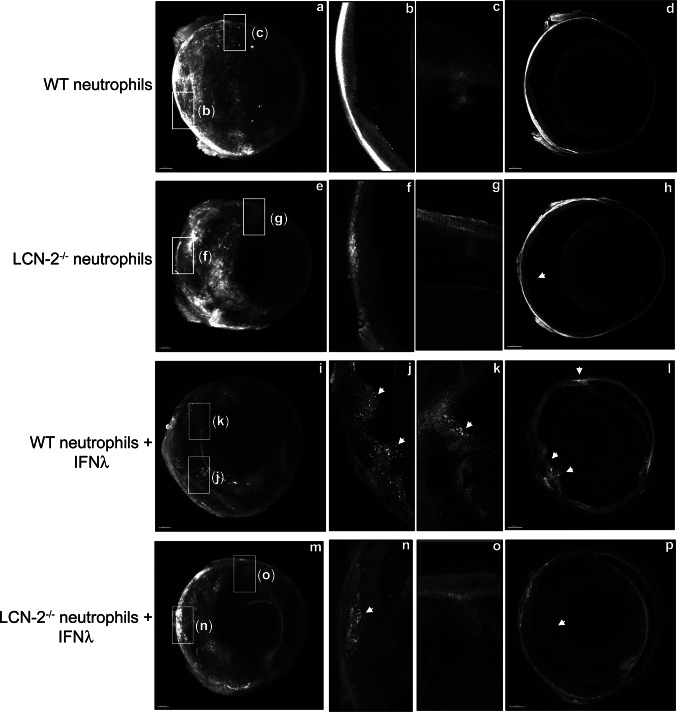
IFNλ triggers neutrophil homing into the eye in vivo. Ribbon scanning confocal microscopy (RSCM) was used to image neutrophil infiltration into whole cleared eyes from NOD-SCID mice intravenously injected with; untreated WT and LCN-2−/− neutrophils or IFNλ-exposed (200 U/ml), WT or LCN-2−/− neutrophils, tagged with red CMTPX. a 3D volumetric and d orthogonal projections from whole eyes obtained from mice injected with, WT neutrophils, did not show neutrophil homing b into the retina or c in through the aqueous humor drainage route (Schlemm’s canal, a channel at the limbus and forms the joining point between the cornea and sclera, encircling the cornea). Mice injected with LCN-2−/− neutrophils showed h prevalence of neutrophils in the eye (arrow), but no infiltration was noticed into the e, f retina or e, g Schlemm’s canal. Mice injected with IFNλ-treated WT neutrophils showed noticeable infiltration of neutrophils into the i, l eye (arrows), particularly in the j retina (arrow) and k Schlemm’s canal (arrow), relative to untreated WT neutrophils. NOD-SCID mice injected with IFNλ-exposed LCN-2−/− neutrophils showed relatively lower numbers of neutrophils in the eye (arrow) (m, p), with respect to IFNλ-treated WT neutrophils, especially in the n retina (arrow). There was no visible neutrophil infiltration into o Schlemm’s canal. n = 1. Scale bar, 300 μm.
Reproduced with permission from Ghosh et al. [96]