Fig. 3.
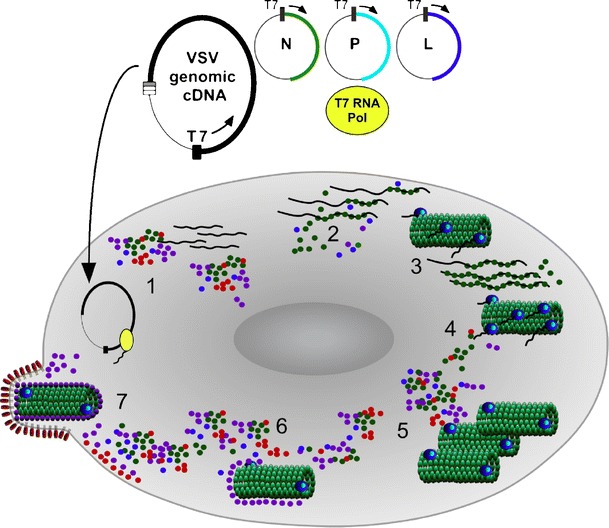
Rescue of rVSV from genomic cDNA. Virus rescue is initiated by cotransfecting plasmids (step 1) encoding the full-length viral genome and transacting viral polypeptides. T7 RNA polymerase, introduced into the cell by a variety of different methods, mediates RNA synthesis in the cell cytoplasm during the earliest stages of rescue, producing copies of the viral genomic RNA and transcripts encoding the transacting polypeptides (N, P, and L) needed to promote de novo assembly of a nucleocapsid (step 2). Functional nucleocapsid subsequently serves as a template for genome replication, transcription of all VmRNAs, and accumulation of viral proteins (steps 3–5) triggering ensuing events in the viral replication cycle including virus assembly (step 6) and budding (step 7)
