Figure 2.
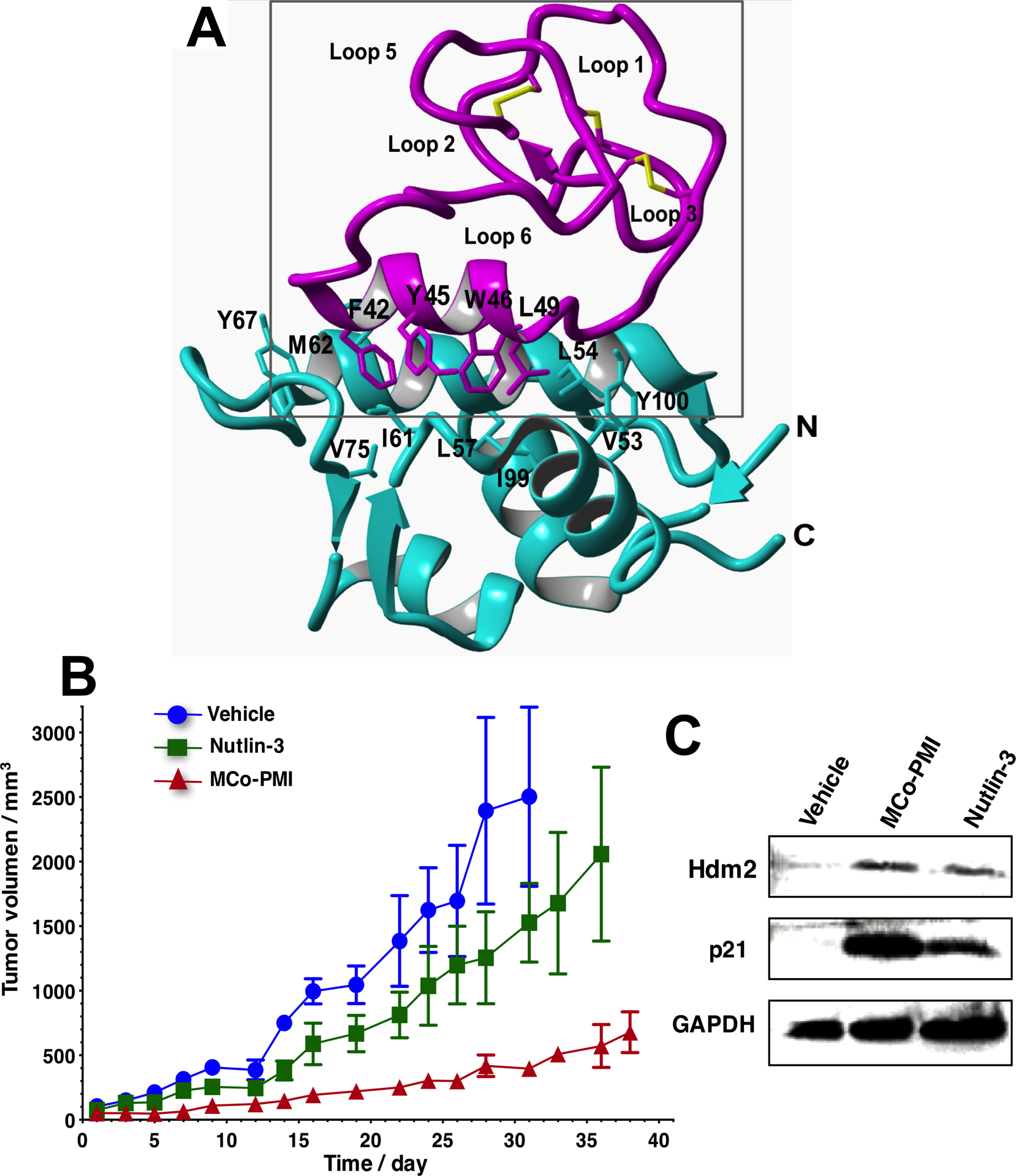
Structure and in vivo activity of the first cyclotide designed to antagonize an intracellular protein-protein interaction in vivo (27). A. Solution structure of the engineered cyclotide MCo-PMI (magenta) and its intracellular molecular target, the p53 binding domain of oncogene Hdm2 (blue) (pdb: 2M86). The cyclotide binds with low nM affinity to both the p53-binding domains of Hdm2 and HdmX. B. Cyclotide MCo-PMI activates the p53 tumor suppressor pathway and blocks tumor growth in a human colorectal carcinoma xenograft mouse model. C. Tumors samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE and analyzed by western blotting for p53, Hdm2 and p21, indicating activation of p53 on tumor tissue.
