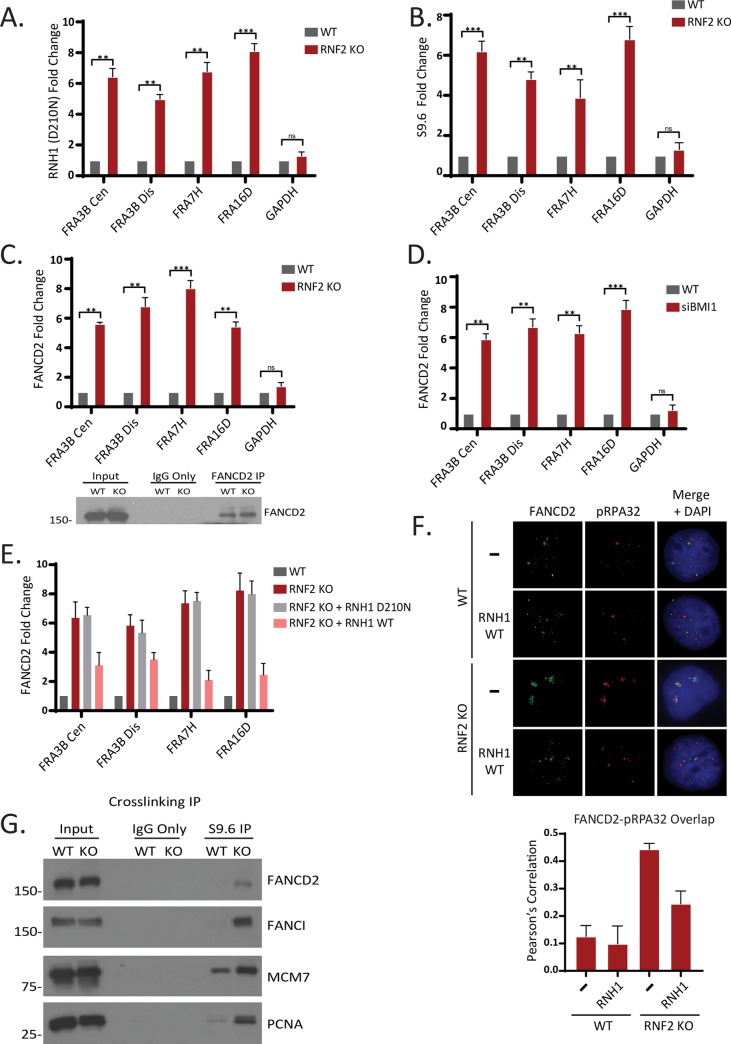
Fig 4. R-loops are accumulated at CFSs and replication forks in RNF2-deficient cells.
A. T80 cells were transfected with pyCAG_RNaseH1_ D210N plasmid and subjected to ChIP with the anti-V5 antibody. qPCRs using indicated primers show that the R-loops are enriched at CFSs in the RNF2 KO cells (N = 3 biological replicates; ***P <0.0005, **P <0.005). B. ChIP using S9.6 antibody and amplification with the indicated primers by qPCR shows that R-loops are increased at CFSs in RNF2 KO T80 cells (N = 3 biological replicates, ***P <0.0005, **P <0.005). C. (Top) ChIP using FANCD2 antibody and amplification with the indicated primers by qPCR shows that FANCD2 is enriched at CFSs in RNF2 KO T80 Cells. (Bottom) Western blot confirming FANCD2 expression and IP efficiency in T80 WT and RNF2 KO cells (N = 3 biological replicates; ***P <0.0005, **P <0.005). D. ChIP using FANCD2 antibody and amplification with the indicated primers by qPCR shows that FANCD2 is enriched at CFSs in BMI1 Knockdown T80 Cells. (N = 3 biological replicates; ***P <0.0005, **P <0.005). E. ChIP using FANCD2 antibody and amplification with the indicated primers by qPCR shows that FANCD2 enrichment at CFSs in RNF2 KO T80 cells is reduced by expressing exogenous RNH1 WT. There was no significant change upon expressing RNH1 D210N (N = 3 biological replicates). F. (Top) Representative images of FANCD2 and RPA foci in WT and RNF2 KO cells. Where indicated, cells were transfected with pyCAG_RNaseH1_ WT plasmid. (Bottom) Quantification of overlap between the FANCD2 and RPA signals by Pearson’s correlation (N = 50 from 3 biological replicates). G. T80 WT and RNF2 KO cells were crosslinked, and the lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with the S9.6 antibody and the eluates were analyzed by western blots for indicated proteins.