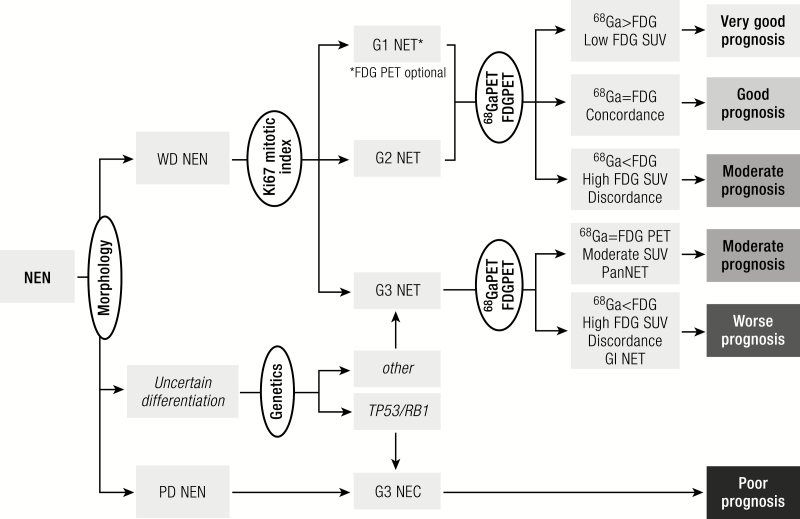
Figure 5.
Diagnostic algorithm. Histology should be obtained from tumors suspected of NEN to confirm the diagnosis of a neuroendocrine origin. Morphological examination will subsequently divide neoplasms into well-differentiated tumors or poorly differentiated carcinomas. Uncertain cases can be categorized through the use of genetic analysis or p53 staining. Within the NETs mitotic and Ki-67 indices will classify the tumor into grade 1 to 3. Further prognostic and therapeutic information can be obtained by performing 68Ga-labelled somatostatin receptor imaging and for higher grade or clinically aggressive tumors an 18F-FDG PET. FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose NEN, neuroendocrine neoplasm; WD, well-differentiated; PD, poorly differentiated; NET, neuroendocrine tumor; NEC, neuroendocrine carcinoma; SUV, standardized uptake value; PET, positron emission tomography; Pan, pancreas; GI, gastrointestinal.