Fig. 2. Involvement of TRPC1 during HSV-1 infection.
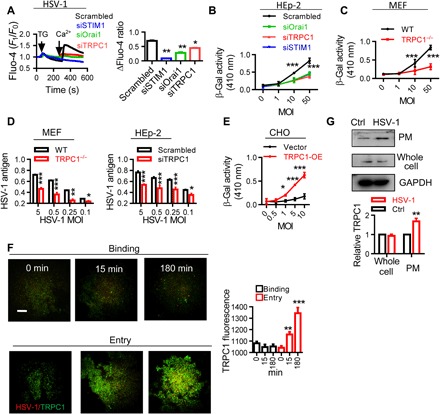
(A) STIM1, Orai1, and TRPC1 are involved in HSV-1–induced SOCE. HEp-2 cells treated with siOrai1, siTRPC1, or siSTIM1 were infected with HSV-1 at 0.5 MOI for 15 min, and SOCE was analyzed as described in Fig. 1B. (B) STIM1, Orai1, and TRPC1 are involved in HSV-1 entry. Entry of HSV-1 into HEp-2 cells treated with siOrai1, siTRPC1, or siSTIM1 was analyzed with β-Gal assays. n = 6 for each treatment, same in (C) to (E). (C) TRPC1 modulates HSV-1 entry. HSV-1 entry into TRPC1−/− MEFs assessed with β-Gal assays. (D) TRPC1 modulates HSV-1 replication. HSV-1 replication in TRPC1−/− MEFs (left) or siTRPC1-treated HEp-2 cells (right) was analyzed by ELISA. (E) TRPC1 enables HSV-1 entry into CHO cells. CHO cells were transfected with TRPC1 overexpression vector (TRPC1-OE), and HSV-1 entry was assessed with β-Gal assays. (F) HSV-1 entry triggers TRPC1 translocation. Increased TRPC1 (green) in the PM during HSV-1 binding or entry into HEp-2 cells was visualized by TIRF microscope. Scale bar, 10 μm. For each condition, data were obtained from three replications, each of which included 5 cells, meaning a total of 15 cells per condition. (G) HSV-1 entry triggers TRPC1 surface expression. Left, representative blots; right, quantitation of TRPC1 surface expression. n = 3 blots for each treatment. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA (A and F), two-way ANOVA (B to E), or unpaired t test (G). Graphs show the mean ± SD.
