Fig. 5. Targeting gD-TRPC1 interaction and TRPC1 translocation to inhibit HSV-1 infection.
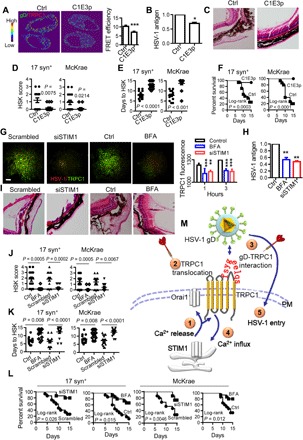
(A) Representative images (left) and statistics (right) of the effect of C1E3p on the gD-TRPC1 interaction. HSV-1 at 0.5 MOI was incubated with 10 μM C1E3p or PBS and then used to infect HEp-2 cells for 15 min. Colocalization of TRPC1 and gD was analyzed by FRET. For each condition, data were obtained from three replications, each of which included 5 cells, meaning a total of 15 cells per condition [same for (G)]. (B) Effect of C1E3p on HSV-1 replication as analyzed by ELISA. HEp-2 cells were infected with HSV-1 as in (A) (n = 6 for each treatment). (C) Effect of C1E3p on HSV-1 infection–induced eye abnormality. 17 syn+ (104 pfu per mouse) or McKrae HSV-1 (103 pfu per mouse) was preincubated with 10 μM C1E3p and then used to infect mice. The C1E3p treatment was repeated every 2 days. Figures show representative eye ball morphology caused by McKrae infection on day 5; magnification, ×40; n = 15 for each infected group. (D to F) Quantitation of effect of C1E3p on in vivo HSV-1 infection. The mice were infected with C1E3p-treated HSV-1 as in (C). HSK scores on day 5 of HSV-1 infection (D), days to HSK causing 50% corneal opacity (E), and survival rates (F) were analyzed. (G) Effect of BFA or STIM1 knockdown on TRPC1 translocation. Representative TIRF microscopy images (left) and statistics (right) for HEp-2 cells incubated with 5 μM BFA or 10 μM siSTIM1 and then infected with HSV-1 at 0.5 MOI for 15 min. Scale bar, 10 μm. (H) Effect of BFA or STIM1 knockdown on HSV-1 replication. HEp-2 cells were treated as in (G), and HSV-1 replication was analyzed by ELISA. PBS or scrambled siRNA served as control, and their values were normalized to 1 (n = 6 for each treatment). (I) Effect of BFA or STIM1 knockdown on HSV-1 infection–induced eye abnormality. The mice were treated with 5 μM BFA or 10 μM siSTIM1 and infected with 104 pfu per mouse of 17 syn+ or 103 pfu per mouse of McKrae HSV-1. Figures show representative eye ball morphology caused by McKrae infection on day 5; magnification, ×40; n = 15 for each infected group. (J to L) Quantitation of the effect of BFA or STIM1 knockdown on in vivo HSV-1 infection. Mice were treated with BFA or siSTIM1 and infected with HSV-1 as described in (I). HSK scores on day 5 of HSV-1 infection (J), days to HSV-1–induced HSK reaching 50% corneal opacity (K), and survival rates for 15 days (L) were calculated (n = 15 for each treatment). (M) Model of the mechanism of TRPC1-mediated HSV-1 infection. ① and ② At an early stage of HSV-1 infection, HSV-1 entry using resting levels of TRPC1 induces intracellular Ca2+ release, which results in activation of STIM1 and Orai1 channels, and consequently TRPC1 translocation to the PM. ③ and ④ TRPC1 and Orai1 also mediate the SOCE; PM TRPC1 serves as receptor for HSV-1 gD. ⑤ TRPC1 facilitates HSV-1 entry into the host cell. Thus, TRPC1 translocation ② and gD-TRPC1 interaction ④ are possible targets (darts) for suppressing HSV-1 infection. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 by unpaired t test (A, B, D, E, J, and K) or one-way ANOVA (G and H). Graphs show the mean ± SD.
