Fig. 4. PL engram neurons receiving monosynaptic inputs from dCA1 contribute to remote memory.
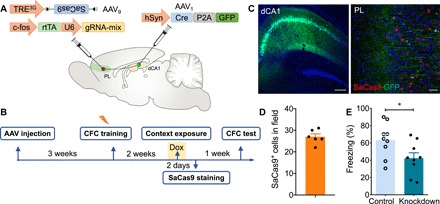
(A) Schematic of the experiment: AAV1-hSyn-Cre-P2A-GFP was injected bilaterally into the dCA1, and a mixture (1:1 ratio) of AAV9-c-fos-rtTA-U6-gRNA-mix and AAV9-TRE3G-DIO-SaCas9 was injected into bilateral PL. (B) Scheme of behavioral test. Rats were trained in the context for fear conditioning 3 weeks after AAV injection. Two weeks later, the rats were given Dox for 1 day and exposed to the context for cell labeling. Recall test was performed 1 week later. (C) Coronal sections showing dCA1 labeled with GFP and PL labeled with Cre- and activity-dependent SaCas9 and dCA1 axons expressing GFP. Scale bars, 200 μm (left) and 50 μm (right). (D) SaCas9+ cell counts in the PL 2 days after context exposure (n = 6 slices from three animals). (E) cbp knockdown in PL engram cells with direct dCA1 inputs decreased the duration of freezing in the probe test (t test, t16 = 2.31, *P < 0.05; n = 9 per group). Rats that were never exposed to Dox served as controls.
