Figure 2.
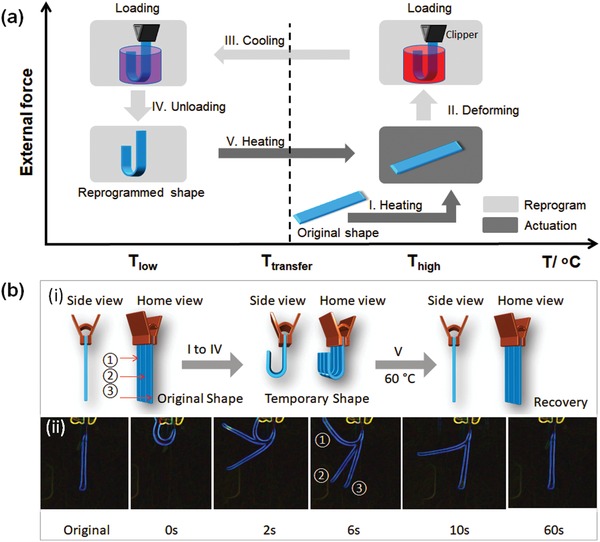
Shape memory properties of the synthesized polymeric materials. a) Illustration of the process of shape memory effect. I, increase the temperature over transition temperature; II, exert a U shape change with enforced restriction; III, fix a temporary U shape at a lower temperature; IV, remove externally enforced restriction; V, increase the temperature to recover the original shape. b) Shape recovery of the synthesized materials. ① BP300D400, ② BP200D600, and ③ BP100D800. i) Illustration of the immobilization of the three samples which are treated with the same conditions. ii) Shape recovery process of V recorded from a side view, displaying the different recovery speeds of the three materials. The images were taken by a camera, and processed with a glowing edge effect. All the samples were bent to U shape at 60 °C and fixed a temporary shape at 23 °C. The shape recovery performed at 60 °C.
