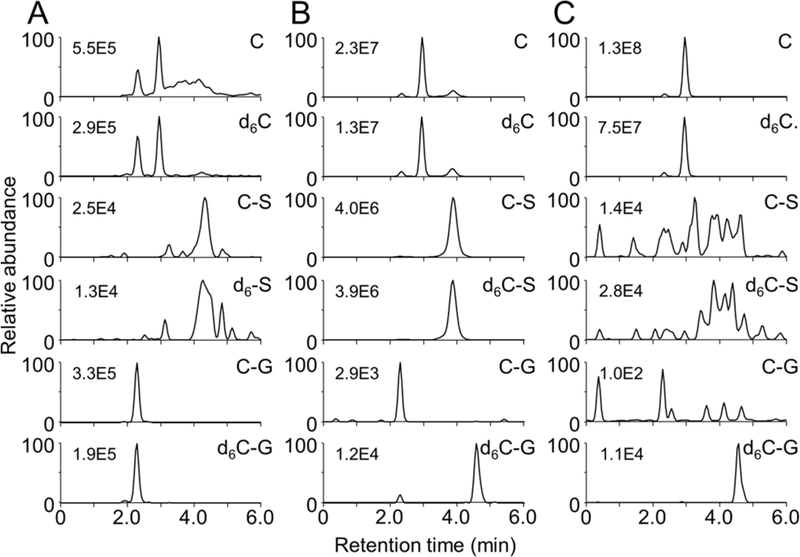
Fig. 3.
LC-MS analysis of curcumin and its conjugate metabolites in serum of mice administered a 1:1 mixture of curcumin and d6-curcumin by i.p. injection. Serum samples were (A) untreated or hydrolyzed with (B) β-glucuronidase or (C) sulfatase prior to extraction. Ion trace chromatograms were acquired using LC-SRM-MS analysis of curcumin (C), curcumin-sulfate (C-S), curcumin-glucuronide (C-G), and their respective d6-isotopologues. Analytical conditions are listed in Table 1. The numbers indicate the highest ion intensity in each trace. The first peak eluting in the C and d6-C chromatograms in (A) is derived from in-source fragmentation of the glucuronide conjugates C-G and d6C-G, respectively, cf. ref. [18].