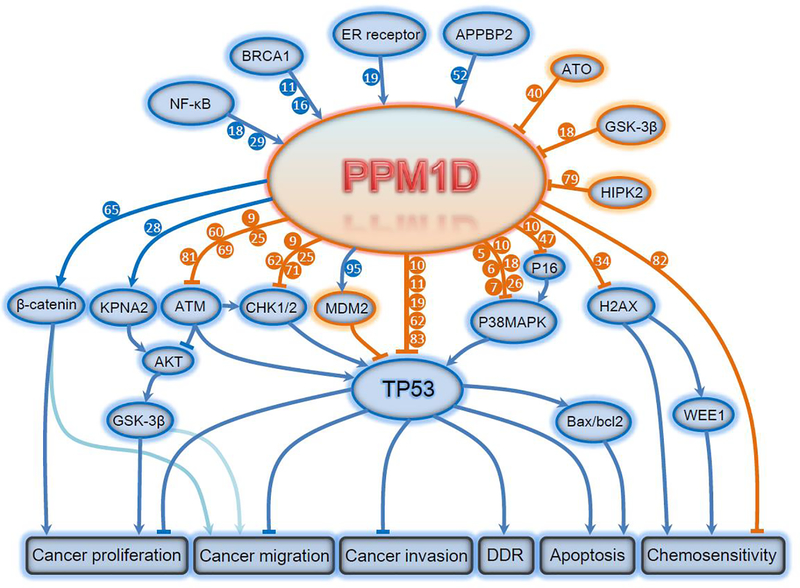
Figure 1. Targets and functional consequences of PPM1D signaling.
The expression and function of PPM1D is regulated by upstream NF-kB, BRCA1, ER receptor, APPBP2, etc. PPM1D phosphatase directly dephosphorylates target proteins including KPNA2, ATM, Chk1/2, Mdm2, p53, p38 MAPK, p16, H2AX and p16, leading to inhibition of apoptosis and promotion of tumorigenesis, invasion, migration and chemoresistance. AKT, AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase; APPBP2, Amyloid Beta Precursor Protein Binding Protein 2; ATM, Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated; ATO, Arsenic Trioxide; BAX, BCL2 Associated X; BCL2, BCL2 Apoptosis Regulator; BRCA1, BRCA1 DNA Repair Associated; CHK1/2, Checkpoint Kinase 1/2; DDR, DNA Damage Response; ER, Estrogen Receptor; GSK-3β, Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta; H2AX, H2A Histone Family Member X; HIPK2, Homeodomain Interacting Protein Kinase 2; KPNA2, Karyopherin Subunit Alpha 2; MDM2, Murine Double Minute 2; NF-κB, Nuclear Factor Kappa B; P38 MAPK, P38 Mitogen Activated Protein Kinases; PPM1D, Protein Phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ Dependent 1D; TP53, Tumor Protein P53; WEE1, WEE1 G2 Checkpoint Kinase.