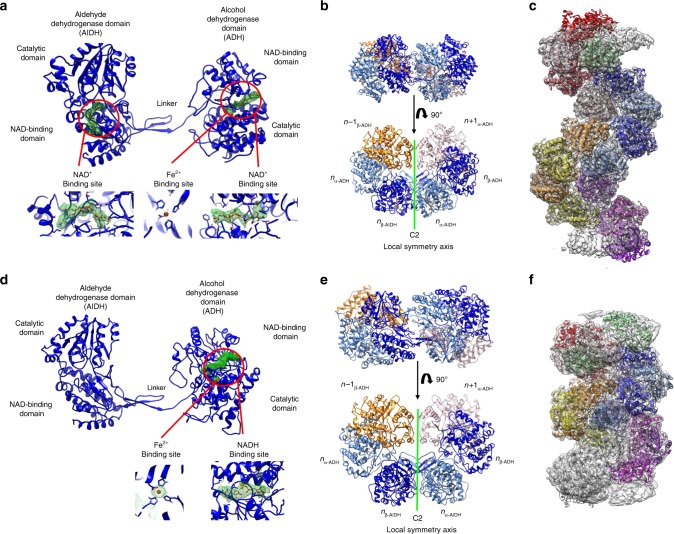
Fig. 2. Structure of AdhE in extended and compact filaments.
a Structure of the AdhE monomer in the presence of NAD+ and Fe2+. The AlDH and ADH domains are identified. In each domain, the electron density corresponding to the NAD+ and Fe2+ is displayed in green mesh, as it is visible in the cryoEM map. In the lower part of the panel, larger views of the cofactor-binding sites are provided. b Structure of the AdhE dimer in its extended conformation. The AdhEn dimer is made of the α (in light blue) and β (in blue) protomers. Each protomer is composed of ADH and AlDH domains. The AdhEn dimer is in interaction with the ADHn − 1 and ADHn + 1. The AdhEα and AdhEβ are related by C2 symmetry. c Structural model of the AdhE filament in its extended conformation. This model was obtained by docking the structure of the AdhE dimer shown in b, in the cryoEM map obtained by HR and by duplicating this dimer along the filament axis using its helical symmetry. d Structure of the AdhE monomer in the presence of NADH and Fe2+. The AlDH and ADH domains are identified. In the ADH domain, the electron density corresponding to the NADH and Fe2+ is displayed in green mesh, as it is visible in the cryoEM map. No density corresponding to the NADH is visible in the AlDH domain active site. In the lower part of the panel, larger views of the ADH cofactor-binding site are provided. e Structure of the AdhE dimer in its compact conformation. The AdhEn dimer is made of the α (in light blue) and β (in blue) protomers. Each protomer is composed of ADH and AlDH domains. The AdhEn dimer is in interaction with the ADHn − 1 and ADHn + 1. The AdhEα and AdhEβ are related by C2 symmetry. f Structural model of the AdhE filament in its compact conformation. This model was obtained by docking the structure of AdhE dimer shown in d, in the cryoEM map obtained by HR and by duplicating this dimer along the filament axis using its helical symmetry.