Fig. 8. Schematic view of the bystander signal communication network.
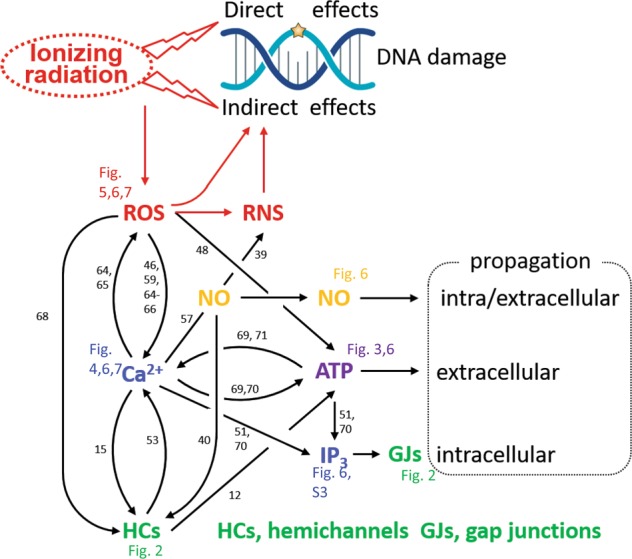
Ionizing radiation directly interacts with DNA molecules and indirectly via radiolysis of water generating ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) produced by ROS interaction with nitric oxide (NO), leading to indirect DNA damage. ROS elevates intracellular Ca2+, and Ca2+ on its turn triggers ROS; Ca2+ also activates synthesis of NO and IP3, and the release of ATP, which drive intracellular and extracellular bystander propagation. IP3 and Ca2+ pass through gap junctions (GJs) while ATP is released via various mechanisms including hemichannels (HCs) that are opened by ROS, Ca2+, and NO. Numbers refer to reference list; Figure numbers refer to results reported here.
