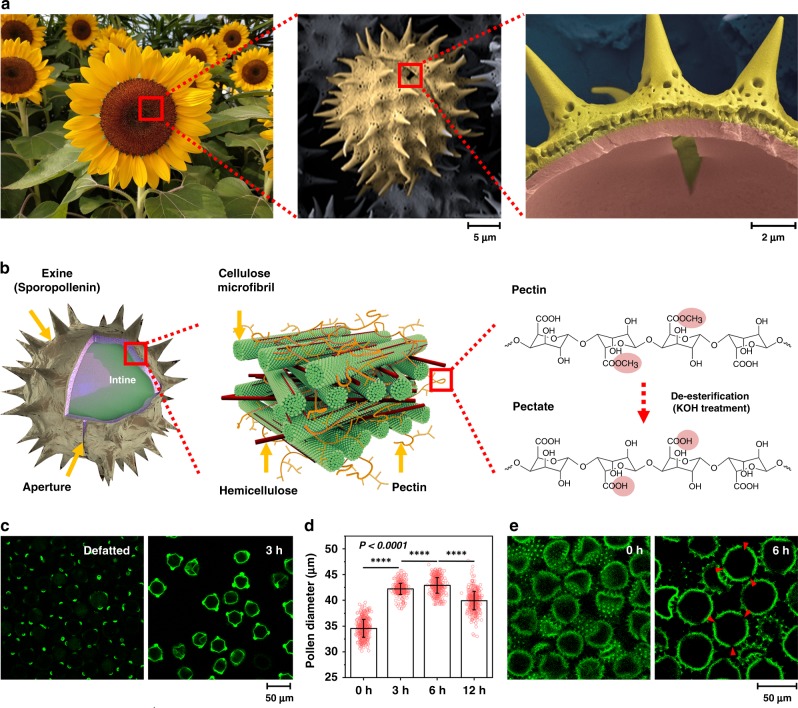
Fig. 1. Engineering dynamic responsiveness in pollen particles.
a Steps involved in the extraction of pollen grains from sunflower plants, shown here with cross-sectional SEM images. The pollen structures are pseudo-colored. b Schematic illustration of stimuli-responsive pollen capsule behavior at multiple length scales. Left: Pollen structural components. Middle: Cellulose microfibrils organized by hemicellulose and pectin in the intine layer. Right: Hydrolytic conversion of pectin to pectate within the intine layer. c Immunofluorescence microscopy detection of de-esterified pectin within pollen shells using JIM5 as the primary antibody. d Size characterization of treated pollen particles as a function of KOH incubation time, as measured by DIPA. Data are analyzed by Student’s t-test and are presented as mean ± s.d. (n = 500 per condition). ****p < 0.0001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. e Cross-sectional CLSM images of pollen-derived microgel particles. Red arrows indicate aperture openings.