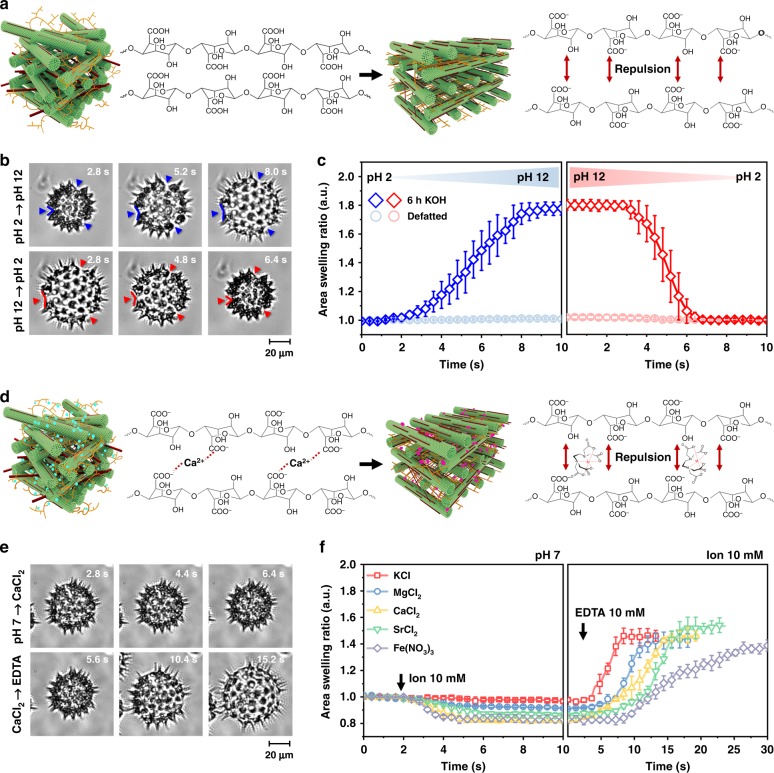
Fig. 2. Tunable pectate interactions enable rapid, stimuli-responsive material properties.
a Schematic illustration of pH-dependent effects on pectin structure and corresponding intermolecular repulsion events. b Time-lapse optical micrographs of tethered pollen particles. The solution pH was changed from pH 2 to 12 (top series), and from pH 12 to 2 (bottom series). c Quantitative comparison of pH-induced pollen swelling and de-swelling behavior. d Schematic illustration of cation-induced attraction and EDTA chelating agent-induced repulsion between pectin molecules. e Time-lapse optical micrographs of tethered pollen particles. Calcium ions were added (top), followed by EDTA chelating agent (bottom). f Quantitative comparison of ion-induced pollen de-swelling and swelling behaviors. Mean ± s.d. are reported (n = 5 particles) in c and f, and the area swelling ratio was normalized by the initial area at pH 2 and pH 7 in c and f, respectively. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.