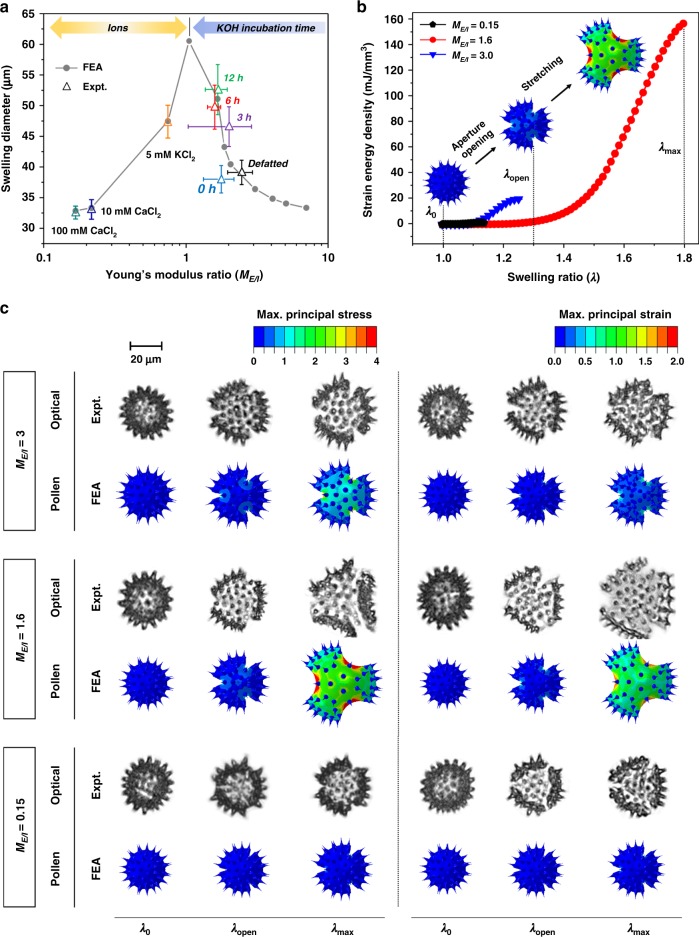
Fig. 3. Mechanical response of pollen microgel particles.
a Swelling diameter of pollen microgel particle as a function of the ratio of the Young’s modulus values of the exine to intine layers, ME/I. b Predicted evolution of the strain energy density during pollen expansion as a function of the swelling ratio (λ) for three typical Young’s modulus ratio values (ME/I = 0.15, 1.6, and 3). c Maximum principal stress and maximum principal strain contours of the pollen microgel particles (ME/I = 0.15, 1.6, and 3) for three critical swelling ratios (λ0, λopen, and λmax) (labeled FEA), along with representative optical micrographs of pollen microgel particles in various chemical environments (i.e., ionic changes) that triggered similar morphological evolutions. ME/I = 0.15 corresponds to pollen microgel particles immersed in 100 mM CaCl2; ME/I = 1.6 to 6 h KOH-treated pollen microgels incubated in pH 10 solution; ME/I = 3 to defatted pollen grains. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.