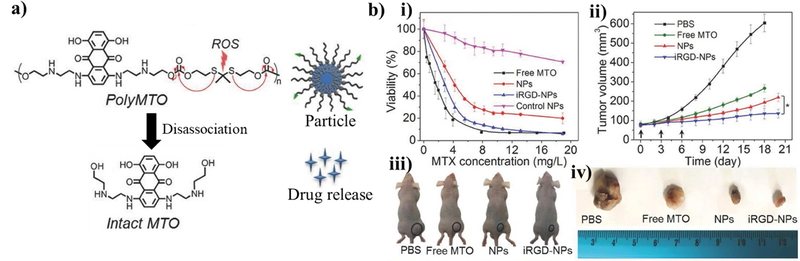
Figure 6. Example particle utilizing thioketal bonds as a ROS-responsive cleavable site.
(a) Schematic of the chemical structure of the mitoxantrone (MTO) polymer made by linking individual MTO monomers with thioketal bonds to form the inner core of the particle. The outer shell consisted of 1,2-distearoylsn- glycero- 3- phosphoethanolamine- N- [methoxy(polyethylene glycol)- 3000] attached with the cell-homing peptide containing RGD sequence. The individual drug molecules could then be released from within the particle when the thioketal bonds are broken in response to surrounding ROS. (b) These particles were shown to target and eliminate tumor cells according to a viability assay and assessment of tumor volume in a mouse model. Reprinted (adapted) with permission from [124]. Copyright 2017 John Wiley and Sons.