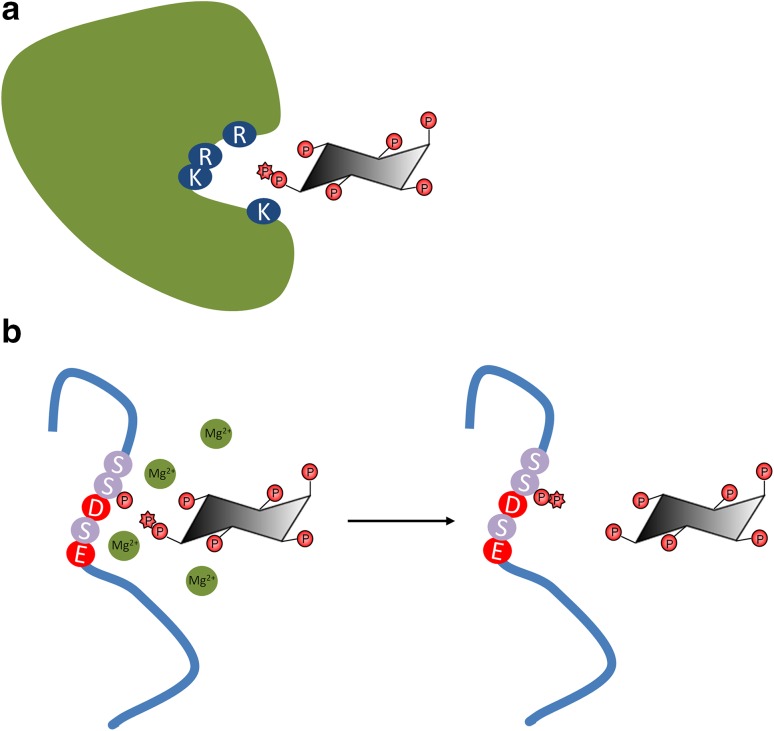
Figure 2:
Mechanism of regulation of protein function by PP-IPs. PP-IPs modulate protein function by two mechanisms: a direct binding to proteins in which the positively charged binding pockets formed by Lys/Arg residues (shown in blue) electrostatically neutralise the high negative charge of the PP-IP molecule,125 and b protein pyrophosphorylation, which involves the non-enzymatic transfer of the β-phosphate from a PP-IP to a pre-phosphorylated Ser residue (shown in mauve) surrounded by Asp/Glu residues (shown in red).