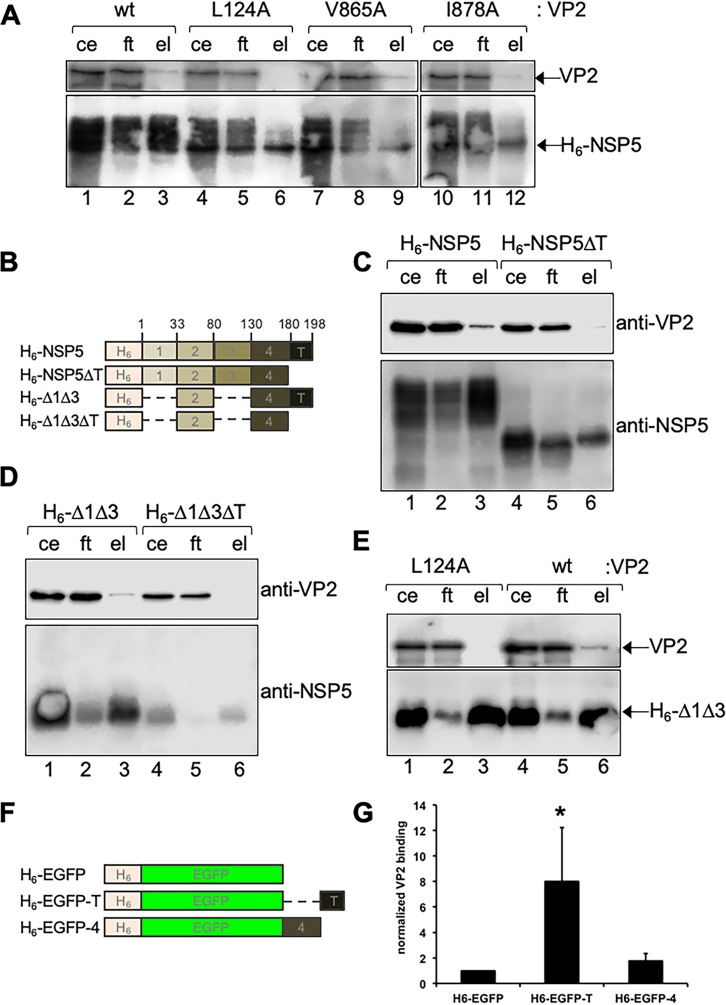
FIG 5.
NSP5 tail and VP2 residues L124 and I878 are required for their association. (A) Immunoblotting of nickel resin pulldown cellular extracts coexpressing histidine-tagged NSP5 (H6-NSP5) with wt VP2 or harboring the indicated point mutation (ce, cellular extract input; ft, flowthrough; el, column eluate). (B) Schematic representation of histidine-tagged (H6)-NSP5 deletion mutants used in panels C, D, and E. Amino acid residues delimiting the NSP5 regions are labeled at the top. Images are not to scale. (C) Immunoblotting of pulldown lysates from cells coexpressing H6-NSP5 (lanes 1 to 3) or H6-NSP5ΔT (lanes 4 to 6) with wt VP2. (D) Immunoblotting of pulldown lysates from cells coexpressing wt VP2 with H6-Δ1Δ3 (lanes 1 to 3) or H6-Δ1Δ3ΔT (lanes 4 to 6). (E) Immunoblotting of pulldown lysates from cells coexpressing VP2 L124A (lanes 1 to 3) or wt VP2 (lanes 4 to 6) with H6-Δ1Δ3. When indicated, the membranes were incubated with anti-VP2 or anti-NSP5 antibody. (F) Schematic representation of H6-EGFP fused to NSP5 regions used in the assay shown in panel E. Images are not to scale. (G) Plot showing the wt VP2 binding to H6-EGFP fused to NSP5 C-terminal regions. Data are represented as means ± standard deviations (SD) from four independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 by Student's t test.