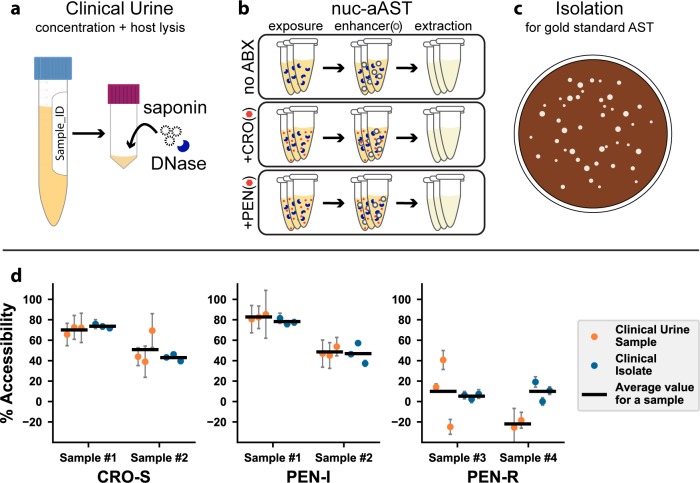
Fig 5. Pilot nuc-aAST with clinical urine samples.
(a) Clinical urine samples were concentrated by a factor of 5 and incubated with DNase I and saponin for 15 min to lyse host cells and clear free DNA. (b) The nuc-aAST protocol was performed in technical triplicates with no ABX, CRO, or PEN. Each nuc-aAST consisted of a 30-min exposure to 1 μg/mL CRO or PEN followed by a 3–5 min exposure to the enhancer TNP (see Methods for details). (c) Each clinical sample was isolated for gold-standard MIC testing and further experiments. (d) Results of six nuc-aASTs were performed directly on four clinical urine samples and susceptibility was determined (orange points). In parallel, isolates were prepared from these clinical samples, and the results of the rapid nuc-aAST with clinical urine samples were compared to the same protocol with the prepared isolate (blue points). The means of the replicates are shown as horizontal lines (S7 Table). The MIC was determined by the gold-standard method (S1 Table). Error bars are the error in the PCR measurement propagated for the calculation of percentage lysis or percentage accessibility (S6 Table). ABX, antibiotic; AST, antibiotic susceptibility testing; CFM, cefixime; CRO, ceftriaxone; CRO-S, CRO-susceptible; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration; nuc-aAST, nuclease-accessibility AST; PEN, penicillin; PEN-I, PEN-intermediate; PEN-R, penicillin-resistant; TNP, TERGITOL NP.