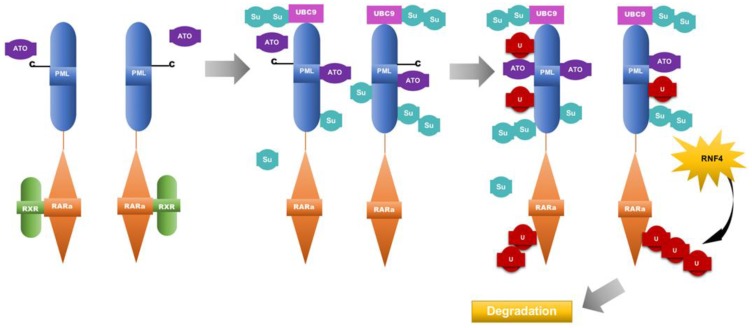
Figure 2. Model for the mechanism of Arsenic trioxide in APL therapy.
Arsenic trioxide binds to cysteine residues on the PML moiety of PML-RARA, triggering the binding of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 9 (UBC9) to the PML RING finger domain. UBC9 recruitment then allows the PML-RARA moiety to undergo sumoylation [19]. The attachment of these ubiquitin-like proteins recruits ring finger protein 4(RNF4) onto PML nuclear bodies [25, 35, 36]. RNF4 is a SUMO-dependent ubiquitin ligase that polyubiquitylates PML, targeting it towards the proteasome for degradation. ATO: arsenic trioxide, RXR: retinoic X receptor, U: ubiquitin molecules, Su: SUMO groups, RNF4: ring finger protein 4.