Figure 2. Principles of filament, motor and cross-link dynamics.
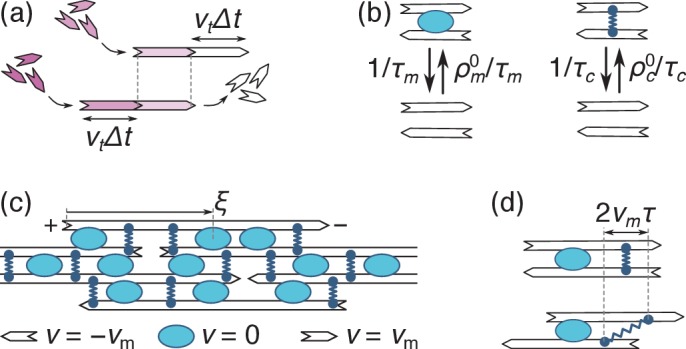
(a) Simultaneous polymerization at the plus end (incoming purple monomers) and depolymerization from the minus end (outgoing white monomers) induce a leftwards ‘treadmilling’ motion of the filament. The top and bottom images respectively correspond to times and . (b) Motors come on and off a pair of filaments with constant rates (on the left), and so do crosslinks (on the right). (c) In an assembly of identical filaments of mixed polarities where motors slide with a velocity , a right-(left-)pointing filament moves with a velocity () relative to any motor. Note that the coordinate is measured from the filament’s plus end. (d) Crosslinks that remain bound to two antiparallel filaments throughout this dynamics stretch with a velocity (the top and bottom panels represent the same system with a time interval ).
