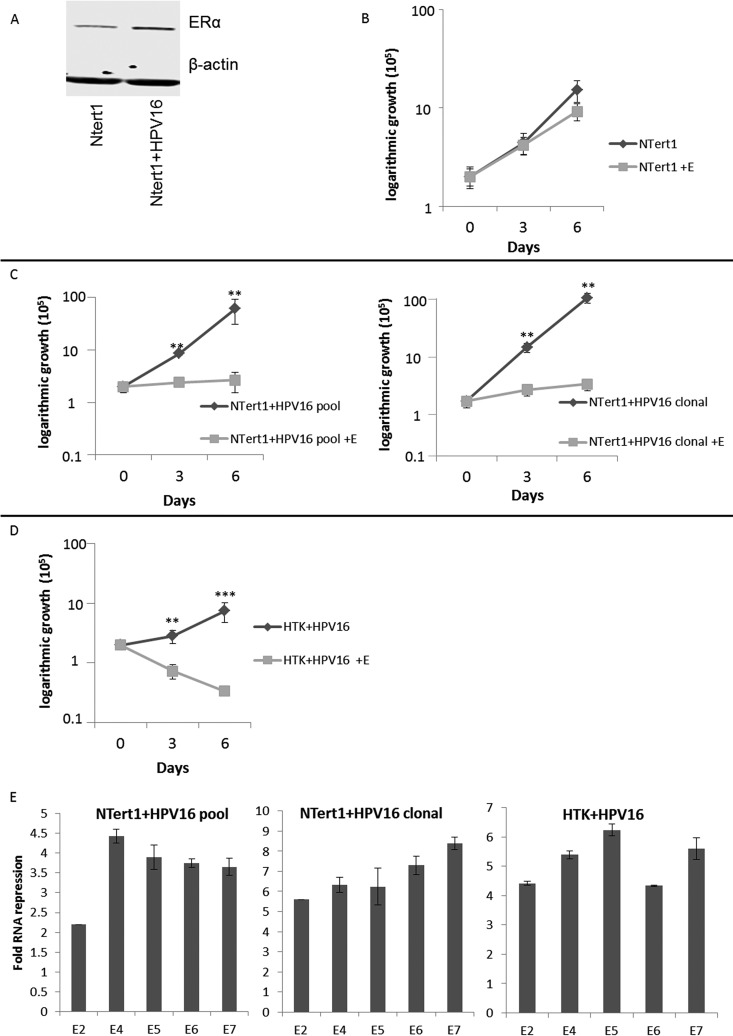
FIG 3.
HPV16 confers estrogen sensitivity to N/Tert-1 cells. (A) Parental N/Tert-1 cell lines and our clonal N/Tert-1+HPV16 cell lines were analyzed for their overall ERα expression levels and compared to the loading control β-actin. (B to D) N/Tert-1 (B), N/Tert-1+HPV16 (pool and clonal) (C), and HTK+HPV16 (D) cells were seeded on day zero and grown in the presence or absence of 15 μM estrogen. Cells were trypsinized and counted on days 3 and 6, and cell counts are presented on a logarithmic scale. Statistical differences can be observed on both days 3 and 6 in all lines except the parental N/Tert-1 cells. **, P < 0.001; ***, P < 0.0001. Experiments were conducted in triplicate and error bars are representative of SE. (E) Pooled N/Tert-1+HPV16, clonal N/Tert-1+HPV16, and pooled HTK+HPV16 cells were grown in the presence or absence of 15 μM estrogen for 7 days. Cells were then harvested, and RNA expression levels were monitored via qPCR for E2, E4, E5, E6, and E7 and compared to the loading control GAPDH. Data are presented as fold repression calculated from ΔΔCT calculated from the comparison of levels observed in control cells and further compared to GAPDH levels. Experiments were conducted in triplicate, and error bars are representative of SE.