Figure 1.
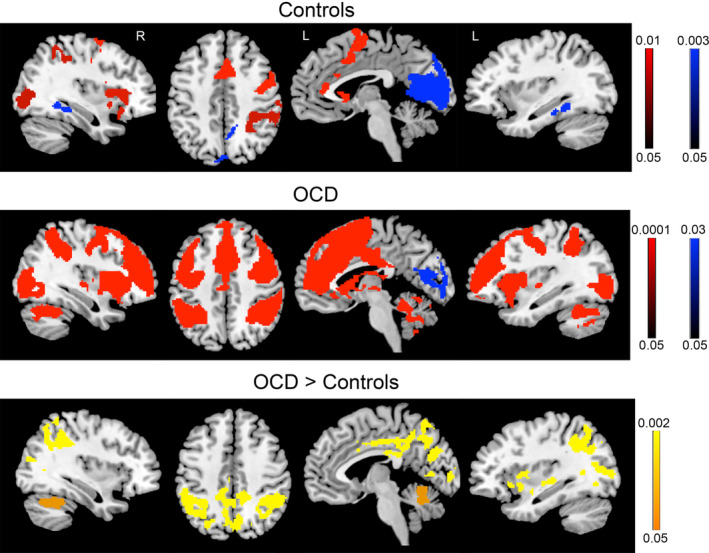
Activity in obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD) patients and controls during early eyeblink suppression. Controls (top panel) and OCD patients (middle panel) for the comparison of early eyeblink suppression > free blinking (red) and free blinking > early eyeblink suppression (blue). Group differences (bottom panel) revealed increased activity in patients compared to controls in the insula, cingulate cortex, inferior parietal cortex, occipital regions, and cerebellum. No significant differences were found for free blinking blocks. Color bars represent whole‐brain family wise error corrected p value
