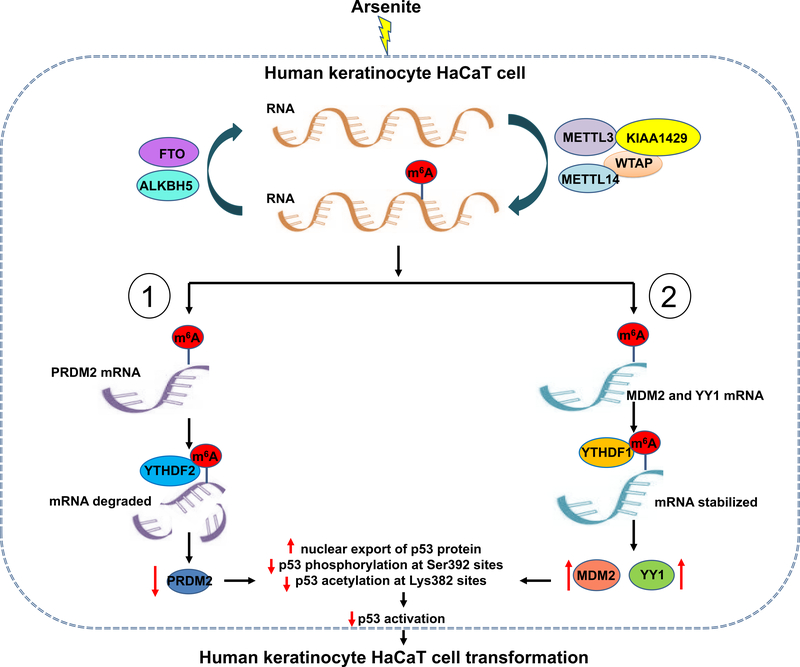
Fig. 7. Model that elevated m6A methylation inhibits p53 activation to mediate arsenite-induced human keratinocytes transformation.
Chronical exposure of arsenite induces the overexpression of m6A methyltransferases (METTL3, METTL14, WTAP, and KIAA1429) and the attenuation of m6A demethylases (FTO), leading to elevated m6A methylation level in transformation of human keratinocytes. Upregulated m6A methylation in p53 positive regulator PRDM2 mRNA binds with m6A reader YTHDF2, inducing the degradation of PRDM2 mRNA and inhibition of PRDM2 expression. Whereas high levels of m6A methylation in p53 negative regulator MDM2 and YY1 mRNA combines with m6A reader YTHDF1, promoting the stabilization and translation of MDM2 and YY1 mRNA. The suppression of p53 positive regulator and the increase of p53 negative regulators induced by m6A methylation contribute to p53 inactivation involved in arsenite-caused transformation.