Fig. 2. Quality of manually reconstructed GEMs from collections without quality control or quality assurance.
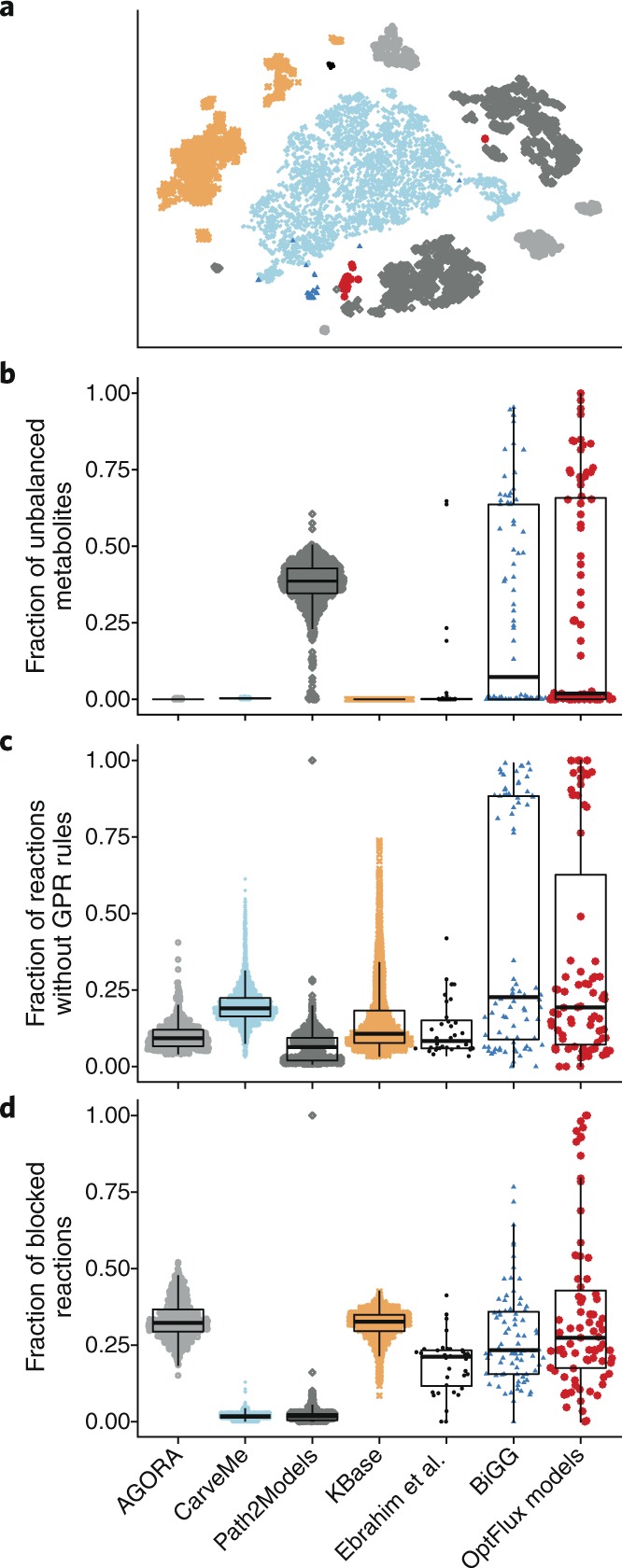
a, Depicted is a t-SNE two-dimensional reduction of models using normalized test features as input. Only GEMs from the BiGG collection form a single albeit small cluster. Models from all other collections are grouped in several fragmented but distinct clusters. b–d, SinaPlots29 of each collection overlaid with box and whisker plots to indicate 25%, 50% (median) and 75% quantiles. GEMs from collections built in a modern automated pipeline (AGORA, CarveMe, KBase) are stoichiometrically consistent, whereas models from the older Path2Models collection are up to 50% stoichiometrically inconsistent (b). Manually reconstructed models (BiGG, Ebrahim et al.30, OptFlux models) contain varying degrees of inconsistent GEMs. GPR rules are essential for in silico knockout studies, but also serve to justify the presence of a reaction (c). Generally, the fraction of reactions without GPR rules is low (~15%). Yet a distinct group of models from the collections of Ebrahim et al. and OptFlux lack GPR rules for >75% of their reactions. Most models from the CarveMe and Path2Models collections contain very few blocked reactions, whereas for models from the other collections the number of blocked reactions lies mostly between 10% and 30% (d). Again, models from the collections of Ebrahim et al. and the Optflux models show the largest variance.
