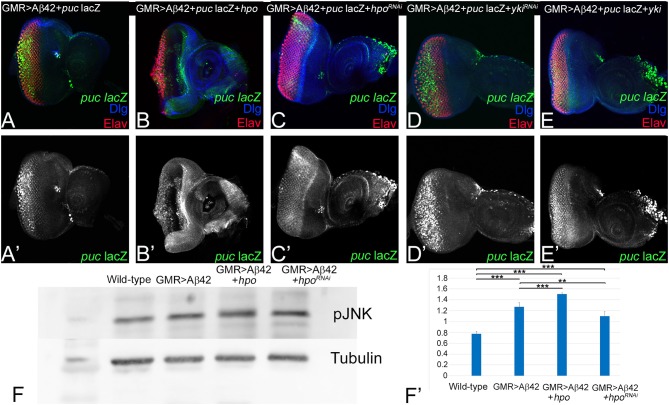
Figure 5.
Activation of Hippo signaling upon amyloid-beta 42 (Aβ42) accumulation also activates c-Jun-amino-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling. (A–E) shows the expression of embryonic lethal abnormal vision (ELAV; red), JNK signaling pathway reporter puc-lacZ (green, gray), and discs large (Dlg; blue) in eye discs from (A,A') glass multiple repeat (GMR)> Aβ42, (B,B') GMR> Aβ42 + hpo, (C,C') GMR> Aβ42 + hpoRNAi, (D,D') GMR> Aβ42 + ykiRNAi, and (E,E') GMR> Aβ42 + yki. For comparison between genotypes, (A'–E') shows puc-lacZ (Gray) levels. (F) A semiquantitative Western blot is presented to show phospho-JNK (p-JNK) levels in the wild-type, GMR> Aβ42, GMR> Aβ42 + hpo, and GMR> Aβ42 + hpoRNAi background. The samples were loaded in the following sequence: Lane 1-Molecular weight marker, Lane 2-Wild-type (Canton-S), Lane 3-GMR> Aβ42, Lane 4-GMR> Aβ42+hpo (gain-of-function), Lane 5-GMR> Aβ42+hpoRNAi (loss-of-function). Alpha-tubulin is used as a loading control, and (F') graph shows the quantification of p-JNK levels, which were calculated from a set of three (n = 3) in wild-type and other indicated genotypes from the Western blot (F). The p-values for estimation of p-JNK levels in all combination in a semiquantitative Western blot was calculated in a set of three (n = 3) using Student's t-test in Microsoft Excel software. The p-value between wild-type and GMR> Aβ42 was significant (p < 0.001; ***), wild-type and GMR> Aβ42+hpo was significant (p < 0.001; ***), and between wild-type (Canton-S) and GMR> Aβ42+hpoRNAi (loss-of-function) was significant (p <0.001; ***). The p-value between GMR> Aβ42 and GMR> Aβ42+hpo was significant (p < 0.001; ***) and between GMR> Aβ42 and GMR> Aβ42+hpoRNAi was significant (p < 0.01; **).