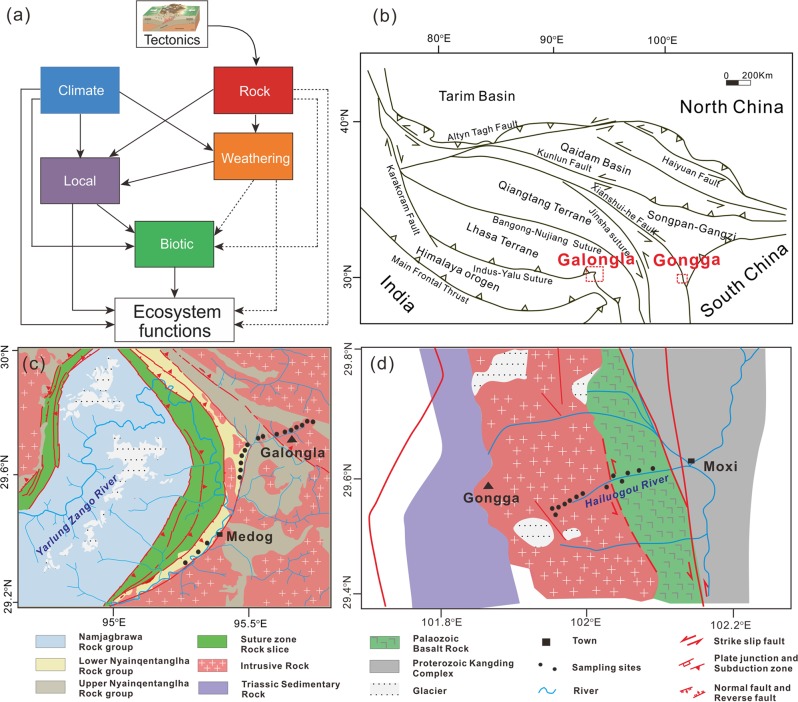
Fig. 1. Hypothesized mechanisms for biological communities and ecosystem functions, and sampling maps.
a Conceptual model showing hypothesized relationships among contemporary environments (e.g., climate, local, and biotic), long-term geological (e.g., parent rock and weathering) processes and ecosystem functions. Solid arrows depict known causal relationships, whereas dashed arrows show the hypothesized but not explicitly documented relationships. b Tectonic map of the Tibetan Plateau showing the locations of Galongla and Gongga mountains. c Sampling sites on Galongla Mountain in Medog, Tibet. This elevational gradient extends across the Indus-Yalu suture zone fault (red lines) bounded by the Himalaya and Gangdese terranes. d The sites sampled on Gongga Mountain by Li et al. [18]. The elevational gradient is intercepted by a secondary Xianshuihe fault (red lines).