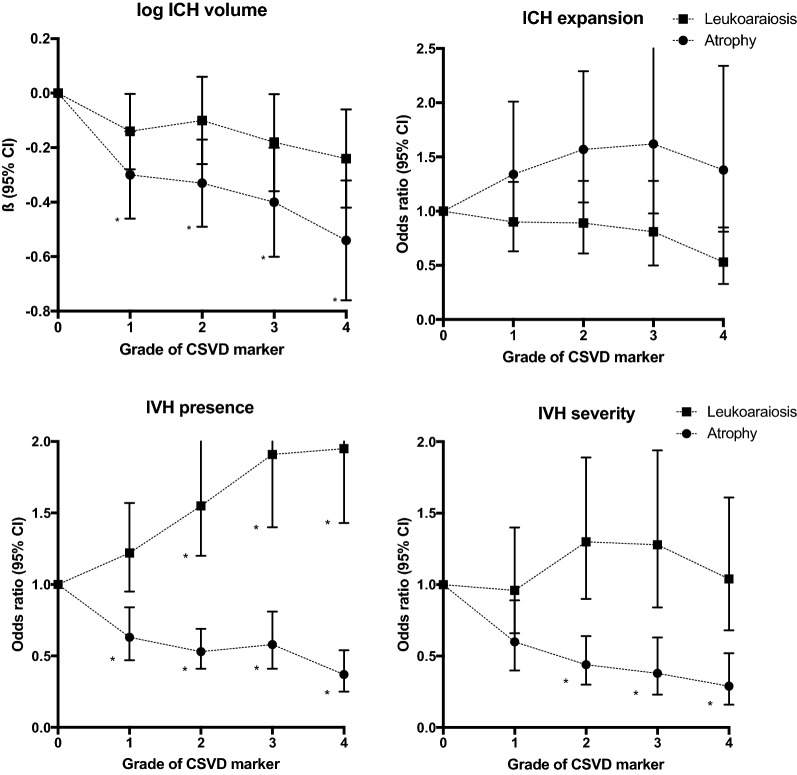
Fig. 2.
Associations of increasing extent of CSVD variables and log-transformed ICH volume (upper left), ICH expansion (upper right), IVH presence (lower left) and the Graeb Score (lower right). All models were adjusted for age, gender, and race ethnicity. In addition, analysis for ICH volume was adjusted for history of stroke, history of alcohol use, time from symptoms to CT, ICH location, and presence of IVH. Analysis for ICH expansion was adjusted for history of stroke, warfarin use, platelet count on admission, time from symptoms to CT, and ICH volume. Analysis for IVH presence was adjusted for serum glucose, ICH location, ICH volume. Analysis for the Graeb Score was adjusted for admission serum glucose. P values considered significant after applying Bonferroni correction are indicated with an asterisk (*). ICH intracerebral hemorrhage, CSVD cerebral small vessel disease, IVH intraventricular hemorrhage