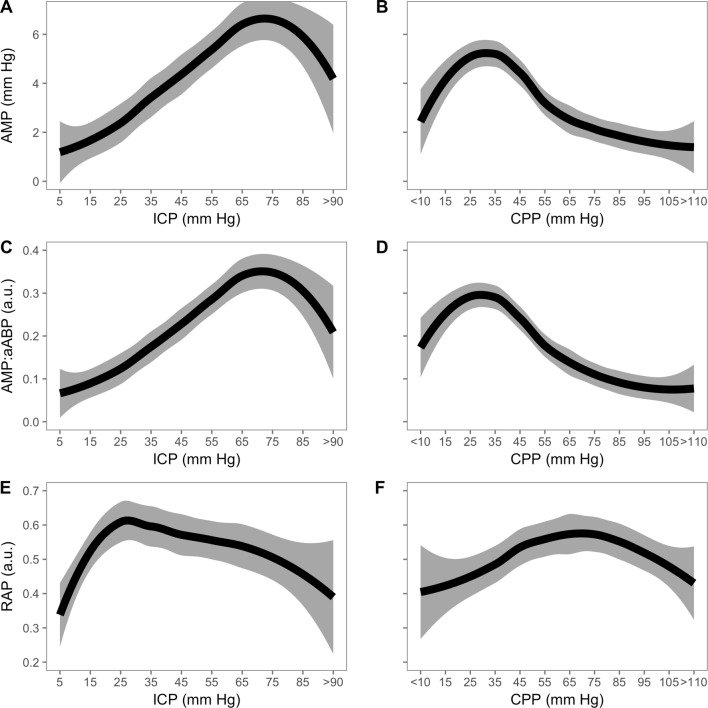
Fig. 4.
Relationship between ICP (left) or CPP (right) with ICP amplitude, transmission of arterial to intracranial pulse, and RAP (LOWESS with 95% confidence interval; n = 33). When all patients are grouped together, an upper breakpoint in the AMP–ICP relationship occurs at around 70 mm Hg. A similar response is seen for arterial to intracranial pulse transmission indicating that a decreased ABP amplitude is not responsible for the AMP-ICP upper breakpoint. RAP increases from low (0 mm Hg) to moderate ICP (~ 30 mm Hg) and thereafter decreases with further increase in ICP. ICP intracranial pressure; CPP cerebral perfusion pressure; RAP cerebrospinal compensatory reserve