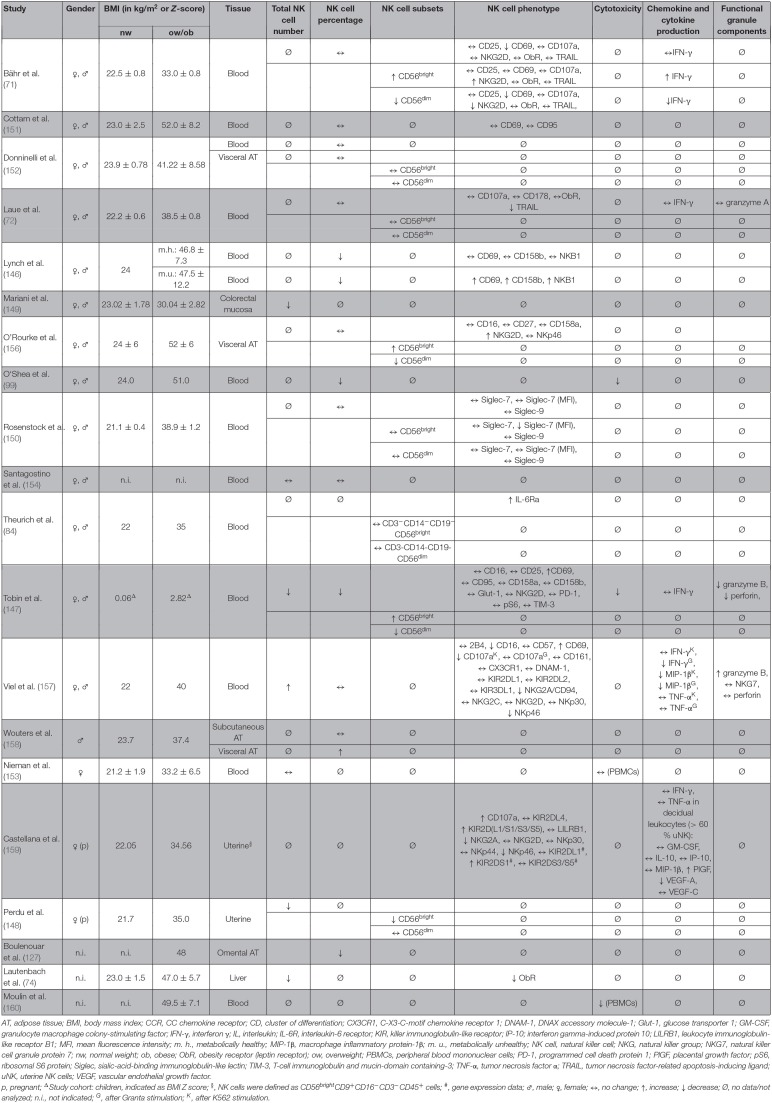
Table 4.
Overview of human studies investigating the effect of obesity on number, subsets, phenotype, and functional parameters of NK cells in different tissues.
AT, adipose tissue; BMI, body mass index; CCR, CC chemokine receptor; CD, cluster of differentiation; CX3CR1, C-X3-C-motif chemokine receptor 1; DNAM-1, DNAX accessory molecule-1; Glut-1, glucose transporter 1; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IFN-γ, interferon γ; IL, interleukin; IL-6R, interleukin-6 receptor; KIR, killer immunoglobulin-like receptor; IP-10; interferon gamma-induced protein 10; LILRB1, leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B1; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; m. h., metabolically healthy; MIP-1β, macrophage inflammatory protein-1β; m. u., metabolically unhealthy; NK cell, natural killer cell; NKG, natural killer group; NKG7, natural killer cell granule protein 7; nw, normal weight; ob, obese; ObR, obesity receptor (leptin receptor); ow, overweight; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PlGF, placental growth factor; pS6, ribosomal S6 protein; Siglec, sialic-acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectin; TIM-3, T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α; TRAIL, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; uNK, uterine NK cells; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
p, pregnant;
ΔStudy cohort: children, indicated as BMI Z score; §, NK cells were defined as CD56brightCD9+CD16−CD3−CD45+ cells; #, gene expression data; ♂, male; ♀, female; ↔, no change; ↑, increase; ↓ decrease; Ø, no data/not analyzed; n.i., not indicated; G, after Granta stimulation; K, after K562 stimulation.