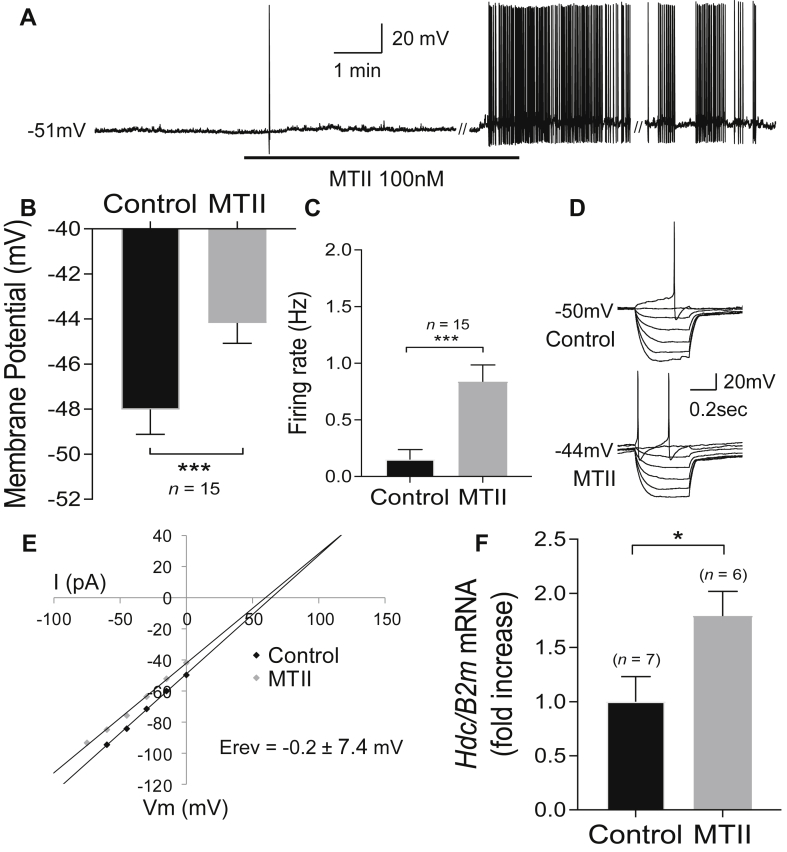
Figure 1.
MTII excites histaminergic neurons. A) Whole-cell current clamp recording showing MTII-induced depolarization and excitation of a HDC neuron. B) MTII induced a significant depolarization of the membrane potential. C) MTII induced a significant increase in firing rate. D) Current voltage relationships of a HDC neuron that was excited by MTII. E) Plot of data shown in D demonstrating a decrease in input resistance. Reversal potential averaged across all HDC neurons excited by MTII suggests activation of a non-selective cation conductance. F) Intracerebroventricular (ICV) MTII significantly increased Hdc mRNA expression in the mediobasal hypothalamus. Note: // denotes discontinuity in the recording (of 35 sec) where current voltage relations were performed. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001.