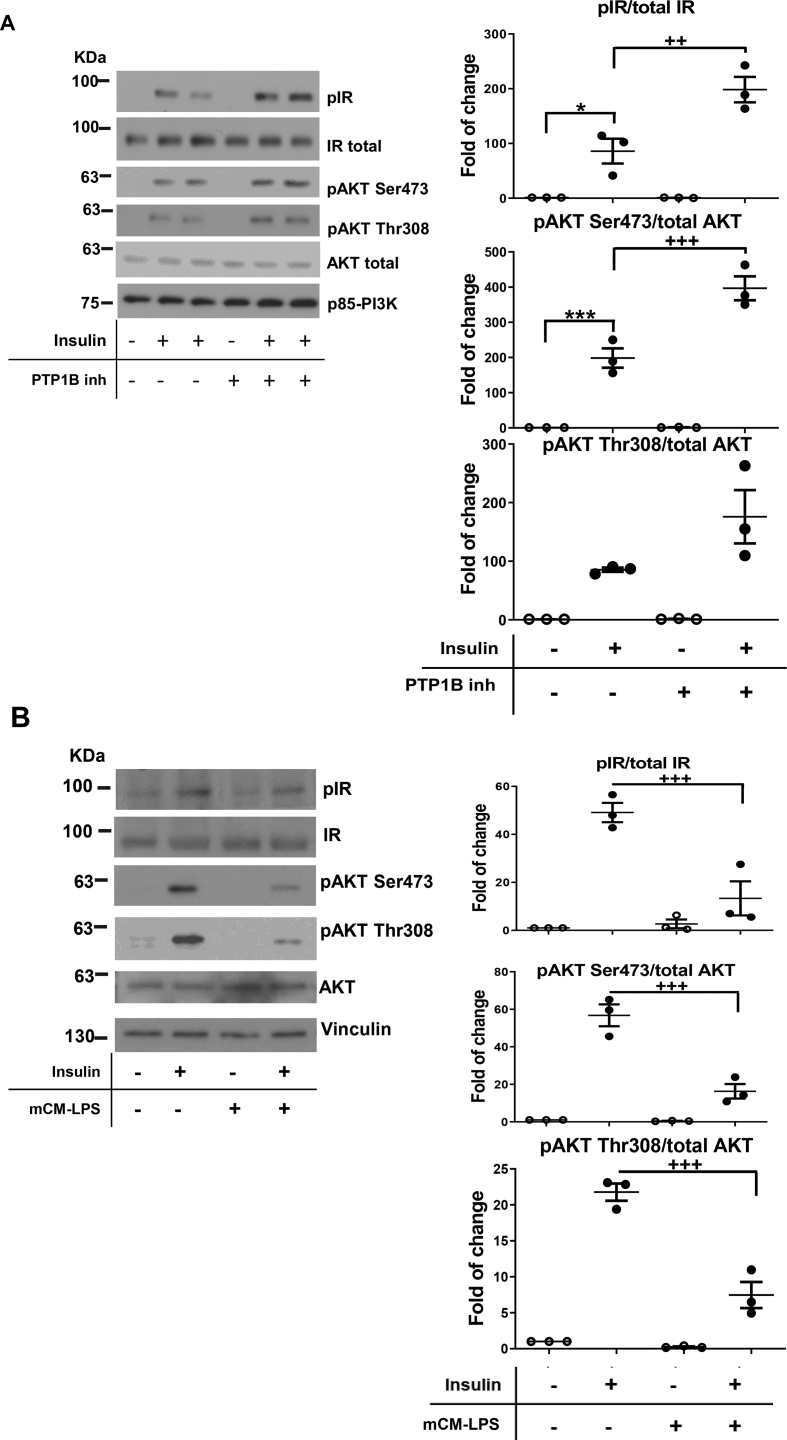
Supplementary Figure 2.
Effect of PTP1B inhibition in insulin signaling in EECs under proinflammatory stimulus. A) STC-1 cells were pretreated or not for 2 h with the PTP1B inhibitor (20 μM) and then stimulated with insulin for 15 min. Protein extracts were prepared, and the phosphorylation of the IR and AKT was analyzed by western blot with the antibodies against phosho-IR, phospho-AKT Ser473, phospho-AKT Thr308, total IR, and total AKT. An anti-p85-PI3K antibody was used as a loading control. Left panel shows representative western blots. In the right panel, graphs show quantification of three independent experiments. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. n=3 independent experiments. ∗p<0.05; ∗∗∗p<0.001 DMEM alone vs insulin; ++p<0.01; +++p<0.001 insulin plus PTP1B inhibitor vs insulin. B) STC-1 cells were pre-incubated with the PTP1B inhibitor (20 μM) before the treatment with mCM-LPS or mCM-C for 16 h. Then, insulin was added for a further 15 min. Protein extracts were prepared and the phosphorylation of the IR and AKT was analyzed by western blot with the antibodies against phosho-IR, phospho-AKT Ser473, phospho-AKT Thr308, total IR, and total AKT. An anti-p85-PI3K antibody was used as a loading control. Left panel shows representative western blots. In the right panel, graphs show quantification of three independent experiments. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. +++p<0.001 mCM-LPS vs mCM-C.