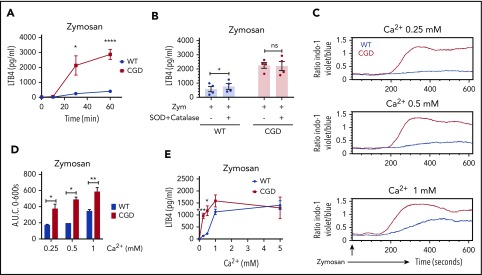
Figure 1.
CGD mouse neutrophils had increased LTB4 production and elevated calcium influx compared with WT, and oxidant scavengers did not increase LTB4 in WT neutrophils. (A) Mouse BM neutrophils (4 × 106/mL) were stimulated for various times with zymosan (MOI = 2 zymosan: 1 PMN) in RPMI 1640 (0.4 mM Ca2+; n ≥ 3). *P < .05; ****P < .0001), by Student t test. (B) Mouse BM neutrophils (4 × 106/mL) were pretreated with 200 U/mL SOD and 200 U/mL catalase for 10 minutes and then stimulated for 1 hour with zymosan (MOI = 2) in RPMI 1640 (0.4 mM Ca2+) in the presence of 200 U/mL SOD and 200 U/mL catalase. n = 4 per group from 2 separate experiments. *P < .05, by paired t test. NS, not significant. (C-D) SOCE in neutrophils from WT and CGD mice was measured by flow cytometry. Mouse BM neutrophils (1 × 106/mL) loaded with 3 µM indo-1 were stimulated with (C) Zymosan (100 µg/mL; MOI ≈ 10) with the indicated amounts of extracellular calcium. (D) Quantification of SOCE (area under the curve [AUC]). Mean ± standard error of the mean from 2 to 4 independent experiments. *P < .05; **P < .01, by Student t test. (E) Mouse BM neutrophils (4 × 106/mL) were stimulated for 1 hour with zymosan (MOI = 2) in Hanks’ balanced salt solution with the indicated amounts of extracellular calcium. LTB4 levels in culture supernatant was measured by ELISA. n ≥ 3 per group from 3 separate experiments. Data are means ± SEM. *P < .01; ***P < .001, by Student t test. MOI, multiplicity of infection.