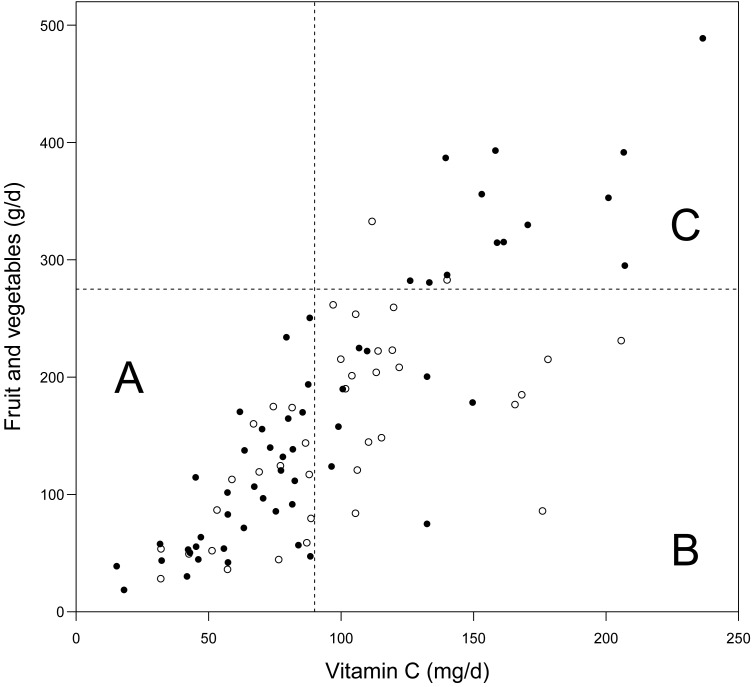
Fig. 2.
Effect of vitamin C intake, and fruit and vegetable intake on the mortality caused by β-carotene (BC) supplementation: participants who initiated smoking at ≥21 years and smoked ≥21 cigarettes/d in male smokers (Alpha-Tocopherol Beta-Carotene Study 1985–1993). ○, Deaths in the placebo arm; ●, deaths in the BC arm. Assuming that BC had no effect on mortality, we would expect a similar distribution of deaths in the placebo and BC arms. The cut-off limits used in the statistical analysis are shown: 90 mg/d vitamin C and 275 g/d fruit and vegetables. The subgroup labels A, B and C are as used in Table 3.