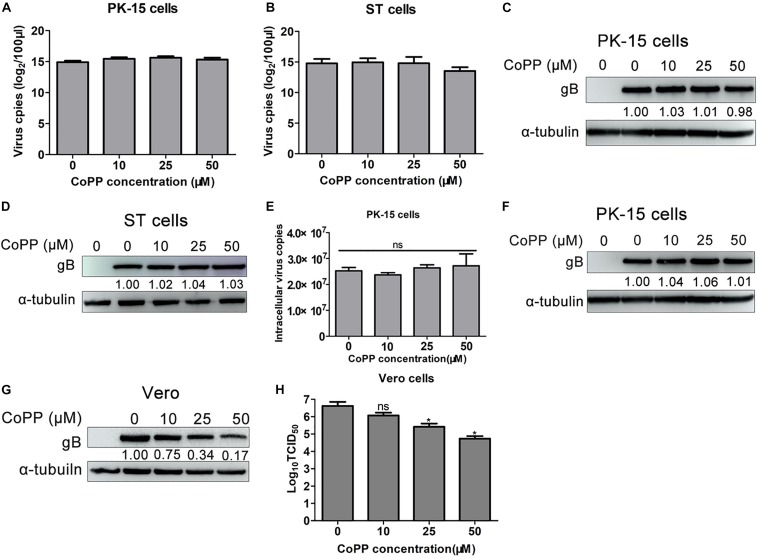
FIGURE 6.
CoPP directly inactivates PRV particles without affecting viral attachment or entry into cells. PK-15 or ST cells treated with 0, 10, 25, 50 μM of CoPP for 12 h at 37°C. After washing three times with PBS to remove residual CoPP, cells were subsequently pre-chilled on ice for 30 min, followed by inoculation with ice-cold PRV (1.0 MOI) for 1 h at 4°C. Cells were washed extensively with ice-cold PBS to remove unabsorbed viruses and analyzed for the virus genome via RT-qPCR (A,B) and for the gB protein via western blotting (C,D). For entry assay, following adsorption with PRV (1.0 MOI) for 1 h on ice, CoPP-treated PK-15 cells were transferred to at 37°C. After 1 h, cells were washed with trypsin to remove virions adsorbed on the cell surface, and subsequently harvested to assess virus genome via RT-qPCR (E) and gB protein expression via western blotting (F). (G,H) PRV virus suspension (0.01 MOI) was co-incubated with CoPP at 37°C for 1 h and used to inoculate Vero cells, and part of the supernatant is directly used to determine the virus titer. After 24 h, cells were harvested for viral replication analysis, and virus titer was tested using TCID50. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. CoPP, cobalt-protoporphyrin; PRV, pseudorabies virus; MOI, multiplicity of infection; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; gB, glycoprotein B.